What is the SCADA? Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) is a centralized system used to monitor, control, and automate industrial processes. In warehouse and logistics automation, SCADA plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operations, minimizing manual intervention, and enhancing real-time decision-making. SCADA integrates hardware and software to collect and process data, allowing supervisors and operators to manage complex systems from a centralized interface.
SCADA is widely used in various industries such as manufacturing, water treatment, energy, oil and gas, and especially warehouse automation, where it bridges the gap between machines and operators.
What are the main components of SCADA?


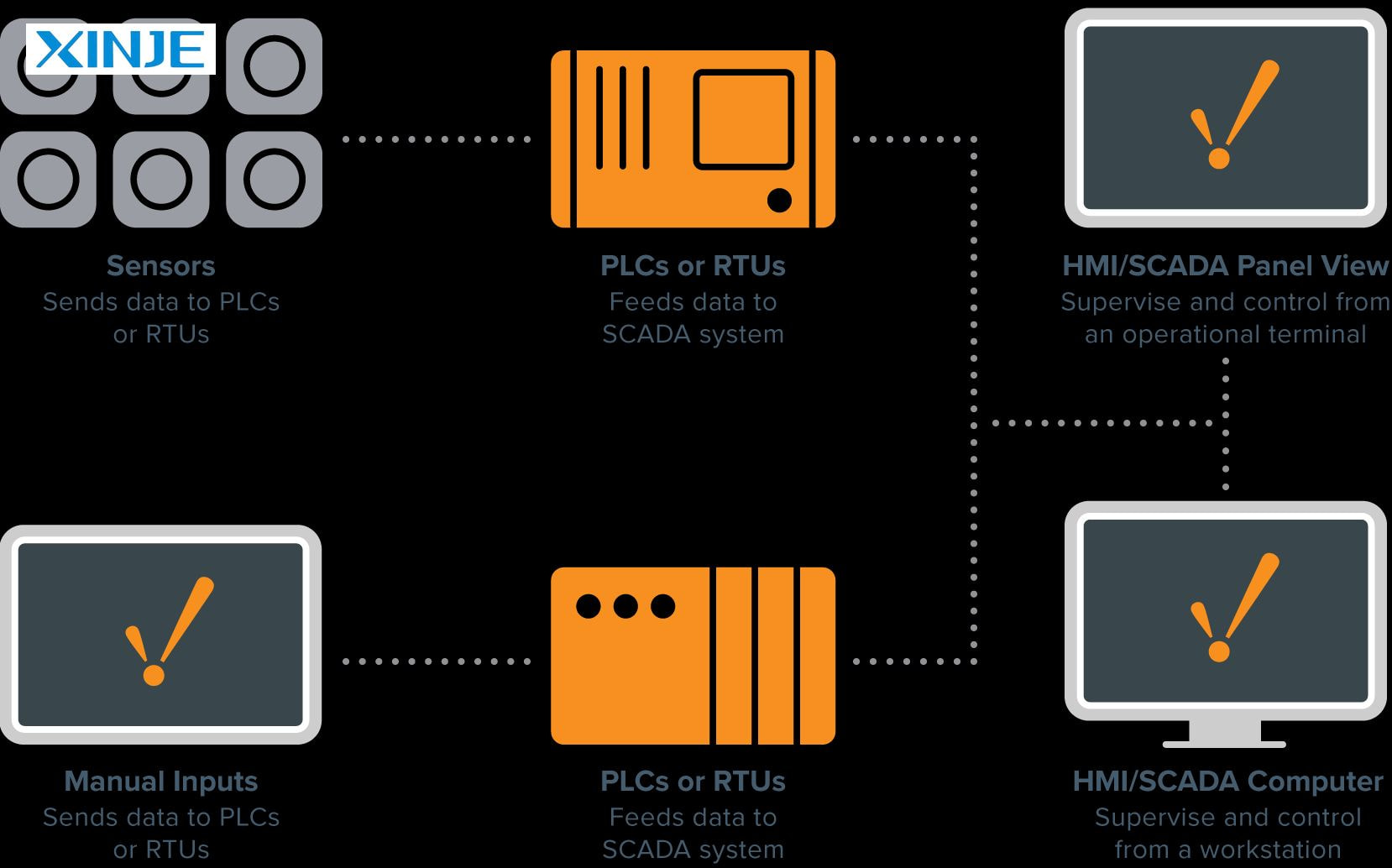
SCADA systems comprise several main components that support one another in operation, data transmission, and analysis, including HMI, SCADA Software, RTU, PLC, Sensors, and actuators.
- Human-machine interface (HMI): A Graphical user interface that allows operators to interact with the system, visualize data, and issue commands.
- Supervisory system (SCADA Software): The central processing unit of SCADA. This system collects data from sensors and devices, records data, and issues control commands.
- Remote terminal unit (RTU): A device that collects data from sensors and transmits data to the central SCADA system. They also receive commands from the SCADA system to control the actuators.
- Programmable logic controller (PLC): Industrial computers that perform real-time machine control. They often operate alongside or in place of remote terminal units (RTUs).
- Communications Infrastructure: Wired or wireless networks that facilitate data transfer between SCADA components.
- Sensors and Actuators: Field devices that detect real-time conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure) and execute control commands.
How does SCADA work?


Due to the combination of many components, the working process of the SCADA system takes place with a certain circuit and usually includes the following steps:
- Data collection: Sensors collect physical data such as temperature, humidity, or conveyor speed.
- Transmission: The RTU or PLC system will transmit the collected data to the SCADA system through a communication network.
- Data processing: SCADA software processes the raw data and displays the data via the HMI panel.
- Control and command: Based on the data and pre-set parameters, the operator or automatic logic commands (e.g., stop the motor, reroute inventory).
- Feedback loop: The system monitors the results in real time and adjusts operations accordingly.
This real-time loop improves operational efficiency, enables predictive maintenance, and supports rapid response to abnormal conditions.
What are the outstanding functions of SCADA?

SCADA will provide a suite of advanced functions designed to streamline operations much more smoothly with special features such as:
- Real-time monitoring: View system performance and status in real time.
- Data logging and trending: Collect historical data for performance analysis and regulatory compliance.
- Alarms and notifications: Alerts to system failures, thresholds, or safety issues.
- Remote control: Operators can issue commands without having to be physically present at the machine.
- Automation: Automate routine control processes to reduce human intervention.
- Integration: Easily integrate with MES, ERP, WMS, and other enterprise systems.
Where is SCADA applied?


SCADA offers many benefits to businesses and is used flexibly in many industrial and infrastructure contexts, including:
- Warehouse automation: Monitoring conveyors, forklifts, autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), and storage systems.
- Manufacturing plants: Monitoring production lines and quality control for easy process management and quality assurance.
- Utilities: Managing water treatment, power distribution, and HVAC systems.
- Oil and gas: Monitoring pipelines and pressure control.
- Transportation: Railway signaling and traffic control systems, equipment that can be easily controlled remotely.
In modern warehouses, SCADA is often the control center of the operation, ensuring that all subsystems, from conveyors to AS/RS units, work in harmony and coordinate with each other.
What are the levels of SCADA?
SCADA systems operate on multiple hierarchical levels. Each level plays a specific role:
Level 0: Field Level: Sensors, Actuators, and Field Devices
This level includes all hardware that collects raw data or executes commands, including proximity sensors, force sensors, motors, valves whose main role is to provide physical interaction with the environment.
Level 1: Control Level: PLC, RTU, performing control tasks
For level 1, real-time logic will be performed to control field devices using coordinated devices such as PLC, RTU, to respond and control immediately based on field-level data.
Level 2: Monitoring Level: SCADA Software and HMI Interface
Level two with centralized software, where operators monitor and supervise processes. The software used mainly at this level is SCADA, HMI screens. Here, the operator will visualize, handle alarms, and control monitoring.
Level 3: Production Level: MES Coordination
Level 3 will have a manufacturing execution system, which interfaces with broader manufacturing planning systems, with the MES platform device managing workflows, production scheduling, and inventory coordination.
How are SCADA and PLC different?
How are SCADA and PLC different?SCADA and PLC are both essential in industrial automation, but they fulfill very different roles within a control system. Understanding their core differences will help determine how each fits into a complete automation strategy. While SCADA and PLC are often used together, they serve distinct purposes:
| Feature | SCADA | PLC |
| Interface | Graphical (HMI, dashboards) | Ladder logic programming |
| Data Handling | Large-scale data logging & analysis | Fast, real-time machine control |
| Scope | System-wide monitoring | Equipment-level execution |
| Flexibility | More flexible in data visualization | More rigid, fixed logic |
| Typical Use | Supervising warehouse systems | Controlling conveyors, lifters, etc. |
SCADA and PLC form a complete automation solution. PLC executes commands, and the SCADA system monitors and optimizes the process. Each type of device has certain features and supports the other.






