In modern automation systems, Graphical User Interface (GUI) – or graphical user interface – is the intuitive bridge between humans and machines. Especially in HMI (Human-Machine Interface), GUI plays a central role in helping technicians easily monitor, control and optimize the production process. So what is GUI in HMI and why is it so important? Let’s find out the details with XINJE in the following article.
General introduction to Graphical User Interface (GUI)
GUI (Graphical User Interface) – also known as Graphical User Interface – is a method of communication between humans and computers through images, icons and visual elements.
Instead of entering commands through lines of code as before, users can easily operate by clicking, touching or selecting icons on the screen.
Especially in the industrial automation industry, GUI is an indispensable component in the HMI (Human-Machine Interface) system. This is the “visual interface” that the operator sees and operates when working with machines.
GUI in HMI helps technicians monitor the status of the production line, receive warnings, control the process – all through the touch screen or control computer.
Common components in GUI include:
- Icon: represents a file, device or function.
- Menu: a set of command options for users to choose from.
- Button: performs a specific action when pressed.
- Graph/Chart: displays real-time data in a visual format.
- Status bar: provides current information or system feedback.

What are the benefits of integrating Graphical User Interface in HMI?
Integrating GUI in HMI system not only improves operational capabilities but also brings many strategic benefits to businesses in the era of industry 4.0:
- Increase work efficiency: Thanks to intuitive GUI display, technicians can quickly understand the status of machinery without having to decode complex code lines or symbols. This helps shorten operation time and error handling.
- Minimize risks and errors in operation: GUI provides clear instructions and warnings in colors or icons, significantly reducing human errors – the factor that accounts for the majority of production interruptions.
- Improve remote monitoring capabilities: Many GUI systems today integrate via web or mobile platforms, allowing factory monitoring from anywhere. This enhances flexible management capabilities, especially useful for factories operating 24/7.
- Support digitalization and digital transformation in the factory: GUI is an important platform to connect HMI with higher-level systems such as SCADA, MES or ERP. From there, businesses can gradually build smart factories, optimizing the entire production value chain.
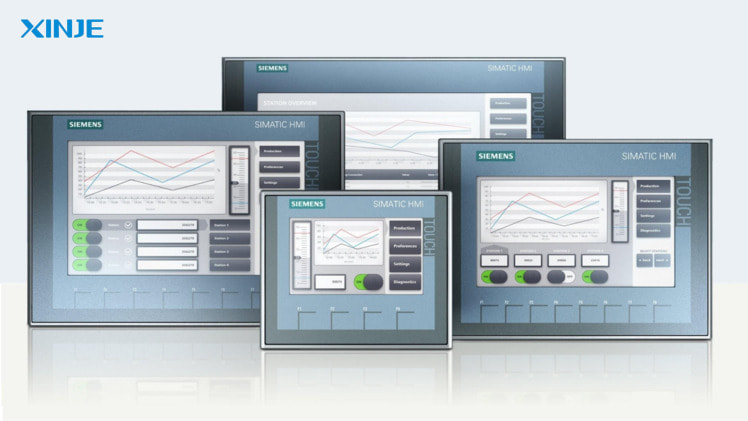


What is the application of Graphical User Interface in HMI system?
In HMI (Human-Machine Interface) system, GUI plays a central role, is the main display for users to interact with machines or production processes.
- Monitoring equipment status and production processes: GUI displays real-time data such as pressure, temperature, motor speed, raw material level, etc. Technicians can easily detect abnormal parameters for timely intervention.
- Control and operate machines remotely: Users can perform operations such as turning on/off equipment, adjusting speed, switching operating modes, etc. directly on the GUI screen without traditional mechanical operations.
- Error warning and problem diagnosis: GUI integrates a warning system with color, sound or pop-up window when an error occurs (eg: sensor signal loss, motor overload, …).
- Display reports and historical data: GUI can be combined with SCADA or MES systems to display charts, production reports, display equipment change trends, … to help managers make accurate and quick decisions.
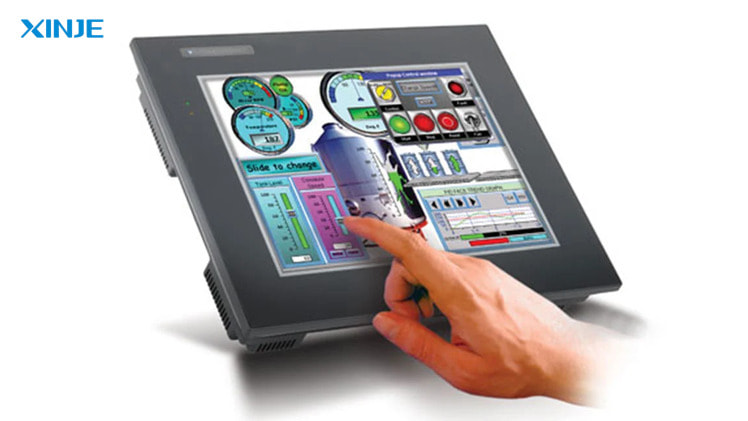


What is the trend of Graphical User Interface design in modern HMI?
Along with the strong development of industry 4.0 technology and smart factories, GUI design in HMI is also constantly improved to meet the increasing operational needs. Not only stopping at data display, modern GUI also focuses on optimizing user experience (UX), increasing interaction and supporting more comprehensive management.
- Multi-touch interface (Touchscreen): Modern HMI interface often uses multi-touch screen, allowing direct operations such as swiping, touching, zooming – similar to when using a smartphone.
- Intuitive, minimalist design: Modern interface aims for the “less is more” style: using easily distinguishable colors, simple icons, clear partitions and optimizing eye flow.
- Dynamic Visualization: Instead of just using text or static data, modern GUIs integrate dynamic graphics that simulate the operation of machines, conveyors, valves, motors, etc. in real time.
- User-based customization: The GUI system allows for decentralization and design of separate interfaces for each user group (technical, supervisory, management, etc.). Thanks to that, each individual only sees the functions appropriate to their role, avoiding confusion or incorrect operations.
- Big data and IIoT integration: Today’s GUI is not only a control interface, but also a gateway to connect data from sensors, PLCs, SCADA to MES or ERP.


Conclusion
In the field of industrial automation, Graphical User Interface (GUI) plays an important role in connecting people with machine systems through an intuitive and easy-to-use interface. When integrated into HMI (Human-Machine Interface), GUI not only simplifies operations but also improves the efficiency of monitoring, warning and controlling the entire production line.
With the trend of modernizing interfaces – from touch, dynamic graphics to big data integration and cross-platform display – GUIs are increasingly becoming an indispensable part of the factory digitalization journey. Therefore, choosing and designing effective GUIs is the key to helping businesses optimize performance, reduce operational errors and develop sustainably in the era of Industry 4.0.






