In the automation and manufacturing industry, cycle time is one of the most important indicators for measuring efficiency and productivity. It shows the time required to complete a product or task and helps businesses optimize processes, reduce costs and increase productivity. With the support of modern technology such as IoT and RPA, optimizing Cycle Time is becoming a vital factor for businesses to maintain a competitive advantage in an increasingly fierce manufacturing environment. This article will help you understand what Cycle Time is, the calculation formula and how to optimize cycle time to achieve the highest business efficiency.
What is Cycle Time?
Cycle Time is among the most important terms in the automation and manufacturing industry. It is defined as the time required to complete a work cycle or produce a product. It is an important indicator to measure the efficiency and productivity in the manufacturing process. Cycle time is also used in ERP and MES systems for production planning.

How to calculate Cycle Time
Cycle Time is the average time required to complete a unit of product or a task in the production line. To calculate cycle time, you can use the following formula:
Cycle Time = Net Production Time / Number of units produced
- Net Production Time: This is the actual time spent on production, excluding downtime, rest or other interruptions.
- Number of units produced: The total number of products completed during the net production time.
Illustrative example:
A manufacturing plant operates for 6 hours per day (360 minutes), but only 300 minutes are actual production time, the rest is spent on machine maintenance and other interruptions. During this time, the plant produces 150 products.
Cycle time = 300 minutes/150 units = 2 minutes/unit
This means that on average, it takes the factory 2 minutes to produce one unit.


What factors affect the calculation of Cycle Time?
Cycle Time is not just a fixed number but depends on many different factors. Understanding these factors helps businesses detect weaknesses and optimize the production process.
- Processing Time: This is the actual time that a job, product or process is performed by a machine or employee. For example: A robot in an assembly line needs 30 seconds to attach a part to a product. This is the processing time.
- Waiting Time: The time that a product or job has to wait between stages of the process due to bottlenecks, lack of materials, or errors in the line. For example: A product is completed at stage A but has to wait 10 minutes before being transferred to stage B because the machine at stage B is busy processing another product.
- Changeover Time: The amount of time it takes to reset a system or machine when changing from one product type to another or changing tools. For example, a packaging line needs to change package sizes, causing the entire line to stop for 15 minutes to adjust.
- Raw material shortages: Shortages or delays in the supply of raw materials or the use of poor-quality materials can increase waiting times and slow down processing speeds.
- Employee expertise: Employees who are not adequately trained or familiar with the workflow can cause delays.
- External factors: Unplanned incidents such as power outages, software errors, or sudden changes in production schedules can also greatly affect cycle times.
Identifying and optimizing each of these factors can not only shorten cycle times but also improve the efficiency of the entire manufacturing process. By understanding the factors that influence them, businesses can develop appropriate strategies to improve productivity, reduce costs and increase competitiveness in the market.


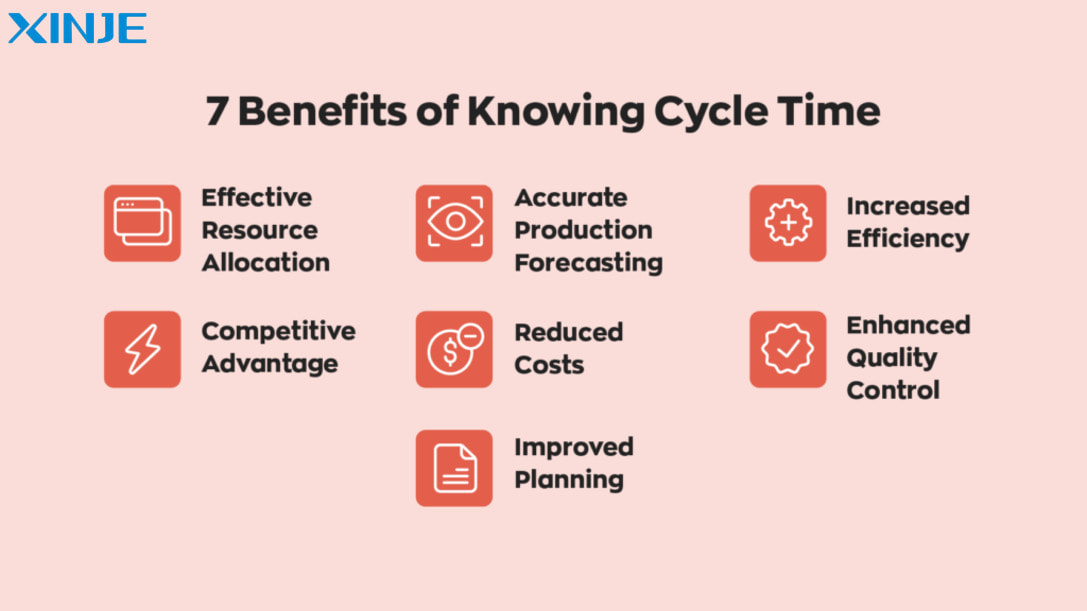
What is the importance of tracking Cycle Time in manufacturing?
- Tracking the manufacturing process: Shorter cycle time means more products can be produced in the same amount of time. This is an important factor in meeting market demand and reducing delivery times.
- Measure and improve performance: Cycle time helps compare actual productivity with the maximum capacity that the line can achieve. This helps identify performance gaps and set improvement targets.
- Identify areas for improvement: Cycle time analysis helps businesses identify inefficiencies in the manufacturing process, thereby optimizing operations to reduce lead times and improve sales. Unusually long cycle times can indicate potential causes of delays, such as machine breakdowns, raw material shortages, or inefficient processes.
- Improve product quality: Tightly controlled Cycle Time reduces the execution time at each stage without affecting product quality, and the product will be more consistent in quality.
- Evaluate operational efficiency: If the cycle time is long, this may reflect unsatisfactory performance, thereby helping businesses detect and adjust in time.
Cycle Time is not only an indicator of time, but also an overall measure of a business’s performance, productivity, and competitiveness. In the automation industry, optimizing Cycle Time is a vital factor to improve efficiency, reduce costs and quickly respond to market needs.

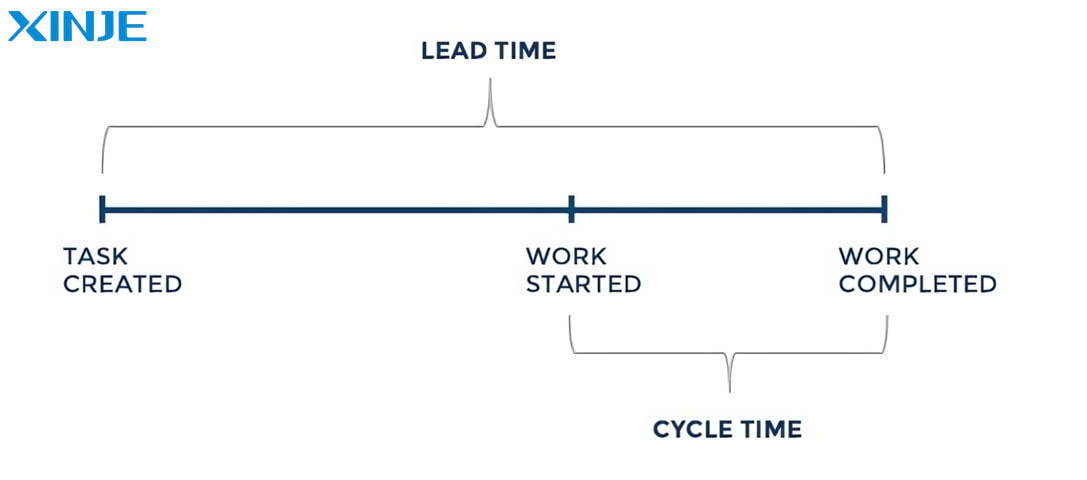
What is the difference between Cycle Time and Lead Time?
In manufacturing and automation management, Cycle Time and Lead Time are two important terms, but they are often confused because they both relate to the time in the manufacturing process. Here is a comparison chart of the differences between the 2 concepts:
| Cycle Time | Lead Time | |
| Definition | The amount of time it takes to complete a product or a step in the manufacturing process. | The total time from when a customer places an order until the product is delivered. |
| Measurement Scope | Only counts actual work time, focusing on value-added activities, not including waiting time or shipping time. | Includes waiting time, non-value-added time, and shipping time, reflecting the entire process from start to finish. |
| Intended Use | Used to optimize manufacturing processes, measure performance at each step, and improve productivity. | Used to track order fulfillment times, manage customer expectations, and optimize the entire supply chain. |

Conclusion
Cycle Time is not only a measurement index but also an important tool to help businesses improve productivity and reduce costs. Understanding the influencing factors and applying modern technology to optimize Cycle Time brings great benefits to businesses in the automation industry.
In the future, with the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), optimizing Cycle Time will become more and more accurate and easier, helping the manufacturing industry achieve new advances.