Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an indispensable device in modern industry. With the ability to flexibly adjust motor speed, save energy, and improve efficiency, VFD optimizes production processes and contributes to environmental protection. In the context of increasing automation and digitalization, VFD will continue to be an important tool, shaping the industry’s future. Let’s look at this device and why it is increasingly popular in modern industries.
What is a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)?
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), also known as a frequency converter, is an electronic device used to control the speed of an alternating current (AC) motor by varying its input frequency and voltage. In the field of automation, VFDs play a key role, helping to optimize energy efficiency, reduce operating costs, and improve process control.
VFDs not only help regulate motor speed but also protect equipment from problems such as large starting currents, overloads, and phase imbalances. Thanks to these advantages, VFDs become the ideal solution in modern industries.


What is the working principle of Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)?
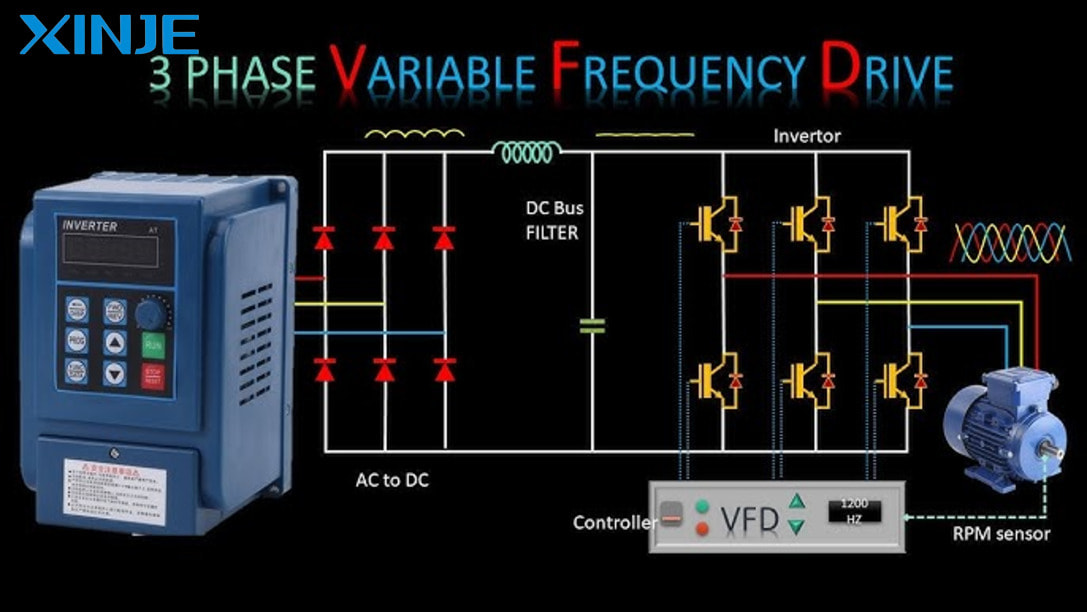
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) works by changing the frequency and voltage of alternating current (AC) to regulate the speed of the motor. This process takes place in three main stages: rectification, filtering (DC Bus), and inversion.
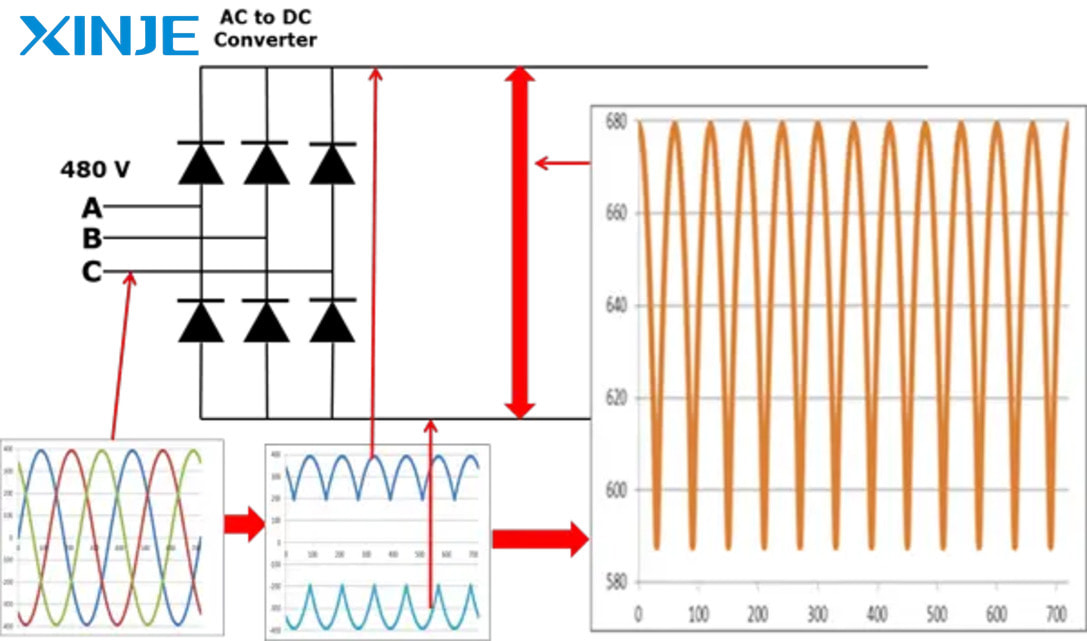
In the first stage, AC power from the grid is fed into the rectifier. The rectifier, usually using a diode bridge or thyristor bridge, converts the AC into direct current (DC). However, the DC at this stage is not stable, still containing many unwanted fluctuations, called DC ripple.
To smooth the DC, the VFD uses a filter consisting of large capacitors and inductors. This filter removes the fluctuations and stabilizes the current before it enters the next stage. The result is a smoother DC, which is the basis for the conversion back to AC with adjustable frequency and voltage.
Next, the stabilized DC is fed into the inverter, where it is converted into new AC. The inverter uses power semiconductor components such as IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) or MOSFET, combined with pulse width modulation (PWM) technology. PWM technology turns semiconductor components on and off very quickly, creating a simulated AC wave with frequency and voltage adjusted according to demand.
Thus, the operating principle of VFD is a flexible combination of electronic components and modern control algorithms, providing precise motor speed control and superior energy efficiency.

How many types of Variable Frequency Drive are there?
VFDs are divided into 3 main types of inverters, depending on the specific requirements of each application, each type of VFD will have its operation and advantages. Understanding the types of VFDs helps you choose the right equipment, ensuring the highest efficiency for your system. Below are 3 common types of VFDs and their characteristics.
Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
- Voltage source inverter (VSI) is the most common type and is widely used in motor control systems. In VSI, the input power is direct current (DC), and it is converted to alternating current (AC) through an inverter.
- Application: Motor control systems such as pumps, fans, and drive systems that require motor speed control.

Current Source Inverter (CSI)
- Current source inverter (CSI) works in reverse to VSI, in which the input source is direct current (DC) with stable current properties. CSI converts this DC current to AC current.
- Application: Systems that require precise torque control such as tractors, air compressors, and heavy-duty drive systems.


Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Inverter Drives
- Pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter drives are a method of controlling frequency and voltage using electrical pulses of variable width. This method is applied in both VSI and CSI to generate alternating current (AC) from direct current (DC).
- Applications: Used in most industrial applications, including pumps, fans, air compressors, and systems that require precise speed control.

What benefits does Variable Frequency Drive provide to businesses?
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) offer many benefits in controlling AC electric motors, from energy savings to performance optimization and equipment protection. Here are 5 key benefits of using VFDs:
- Flexible speed control: VFDs allow for flexible and precise adjustment of motor speed, tailored to the needs of each application. This is important in manufacturing systems or machines that require continuous speed changes, such as conveyors, mixers or cutters.
- Prolonged equipment life: By controlling starting current, reducing mechanical shock and maintaining optimal operation, VFDs help extend the life of motors as well as related components such as bearings, belts and drive systems.
- Smooth starting: When starting a motor using traditional methods, the starting current is often very high, 6-8 times the rated current, causing wear and damage to equipment. VFDs help reduce starting currents by accelerating motors slowly, avoiding electrical and mechanical shocks.
- Optimize production processes: VFDs help regulate and monitor factors such as speed, flow, torque, and pressure, thereby improving the efficiency and quality of the production process.
- Environmentally friendly: VFDs are capable of regenerating energy, helping to increase system efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This makes VFDs an ideal choice in sustainable industrial projects.


When should Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) technology be implemented in a production line?
Using VFDs offers many benefits in industrial and residential applications, helping to optimize performance and save costs. Here are specific cases when you should use a VFD:
- To control motor speed: One of the main reasons for using a VFD is to control motor speed. By adjusting the frequency and voltage of the motor, a VFD allows precise control of motor speed, helping to optimize the production process and meet the technical requirements of each stage.
- To save energy: VFDs allow motor speed to be reduced in applications such as pumps and fans, thereby saving energy effectively.
- To reduce motor overload: When starting a motor without a VFD, the motor will be subjected to a high starting current, which can cause overload and reduce the life of the motor. Using a VFD reduces starting current and instantaneous torque, helping to protect the motor from damage due to overload.
- For precise torque control: VFDs allow precise torque control, which is important in applications where torque needs to be varied dynamically according to job requirements. This is especially useful in heavy machinery applications.