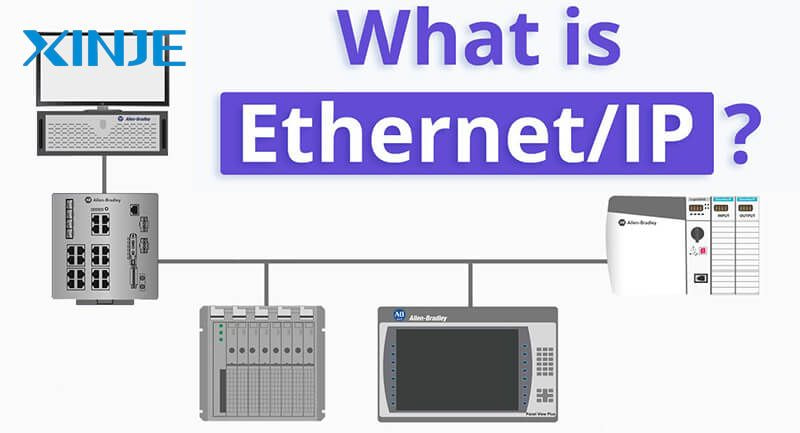
What is the Ethernet/IP HMI? Ethernet/IP (Industrial Ethernet Protocol) is an application layer protocol built on standard Ethernet technologies and is widely used in manufacturing, process control, and robotics systems. When integrated into an HMI, it allows operators to communicate with PLCs and other devices using a reliable, fast, and standardized communication channel.
But what makes Ethernet/IP HMI stand out? Why is it the top choice in factory automation systems? Follow this article and you will have the answer.
What are the benefits of Ethernet IP?
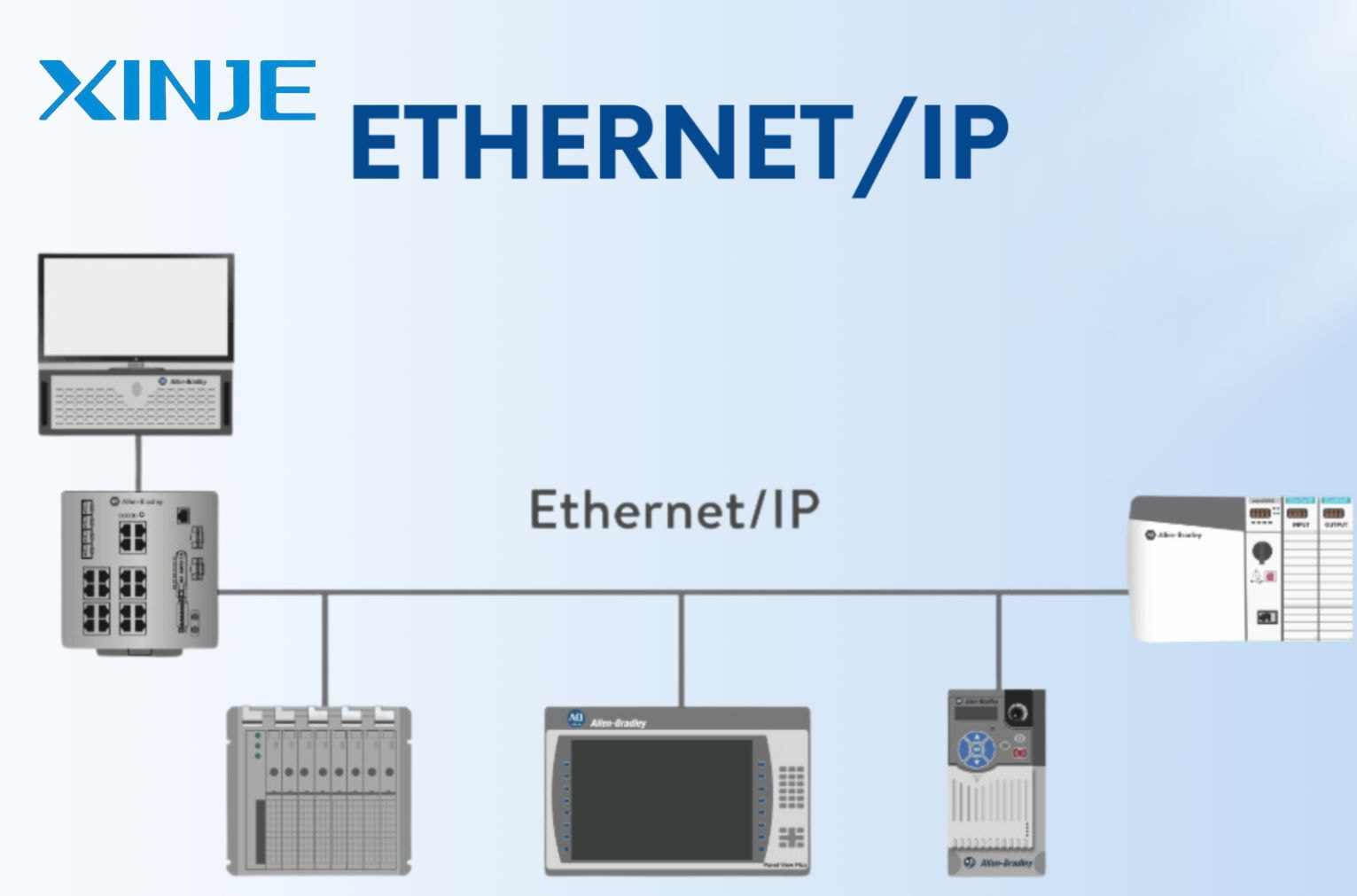

Ethernet/IP is an open protocol managed by the Open DeviceNet Vendor Association (ODVA). Unlike proprietary protocols, Ethernet/IP allows for interoperability between devices from different manufacturers, giving system integrators more flexibility and reducing vendor lock-in. Some of the key features of this protocol include
- Real-time control and high-speed communication: Ethernet/IP allows for deterministic and time-sensitive communication, which is critical for real-time control systems. It supports data rates up to 1 Gbps, making it ideal for applications such as motion control or high-speed manufacturing lines.
- Good scalability: Built on TCP/IP and UDP/IP, Ethernet/IP networks are highly scalable, with setups ranging from simple systems to complex distributed systems, all while using the same protocol. It is the ideal choice for Industry 4.0 and smart factory transformation.
- Cost-effective and easy to deploy: Since Ethernet/IP uses standard Ethernet hardware such as RJ-45 connectors, CAT5e/6 cables, and switches, it reduces both hardware and maintenance costs.
- Built-in Safety and Diagnostics: Advanced features such as CIP Safety and CIP Sync provide built-in safety mechanisms and synchronized timing, enhancing the reliability of automation systems. Built-in diagnostics and logging features make it easy to detect and troubleshoot network or device problems.
Where can Ethernet be used?
Ethernet/IP HMIs are versatile and can be applied in a wide range of industrial and manufacturing environments. Here are some typical applications:
- Factory automation: In discrete manufacturing, Ethernet IP HMIs connect to PLCs, sensors, and drives for real-time machine control, visualization, and fault monitoring.
- Process industries: Industries such as oil and gas, food & beverage, and pharmaceuticals rely on Ethernet IP for SCADA-level HMI operations, allowing operators to monitor variables such as temperature, pressure, or flow across large-scale systems.
- Robots and motion control: Ethernet IP supports the high-speed communication needed to synchronize multi-axis robots, servo systems, and vision-guided automation with HMI feedback and visualization.
- Material Handling Systems: Conveyors, elevators, sorters, and packaging lines benefit from Ethernet/IP HMIs for seamless coordination between machines, reducing downtime and improving throughput.
- Energy and Utility Management: Power plants and renewable energy systems use Ethernet IP to integrate HMI panels into energy monitoring, grid management, and substation control.
How to use an Ethernet IP HMI device?
Using an Ethernet IP-enabled HMI in your automation project involves the following basic steps:
- Device selection: Choose an HMI that supports native Ethernet/IP communication. Brands like Xinje, Allen-Bradley, Siemens (supports multiple protocols)…
- Network setup: Connect the HMI and PLC/controller to the same Ethernet network. Use industrial-grade Ethernet switches to ensure reliable communication.
- Tag configuration: Most Ethernet/IP HMIs allow tag-based addressing, making it easy to map controller variables (such as motor speed, temperature, and pressure) directly into the HMI project. This streamlines communication and reduces programming time.
- Screen development: Use the HMI manufacturer’s software to build intuitive interfaces with buttons, gauges, alarms, and trend charts that interact well with the previous tag configuration.
- Test and Go-Live: Before deployment, simulate the communication between HMI and PLC. Ensure data values are updated correctly, alarms are triggered, and user inputs are recorded in real-time.
What is the difference between Profinet and Ethernet IP?
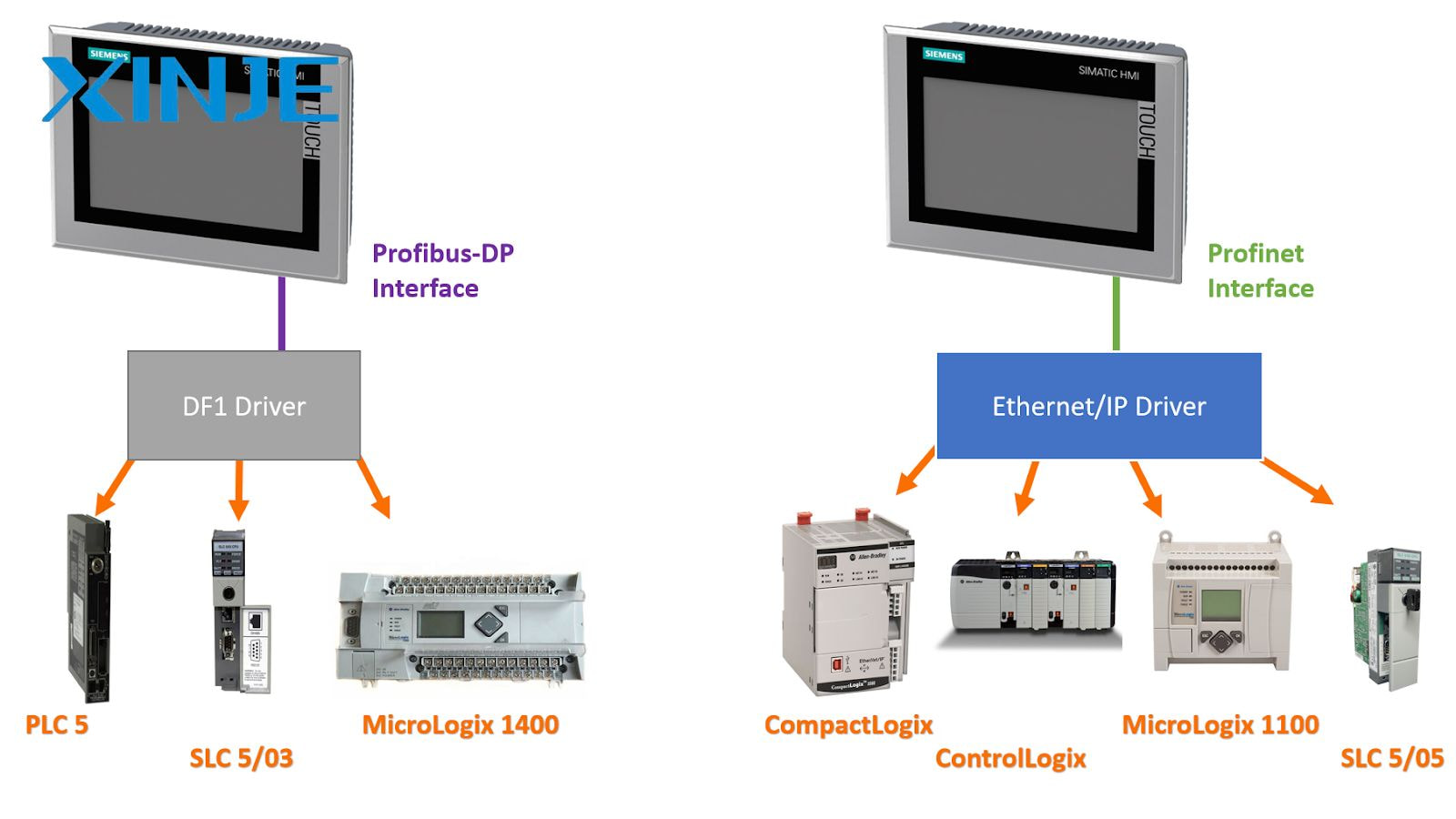

Both PROFINET and Ethernet/IP are leading industrial Ethernet protocols that are widely used and deployed in automated manufacturing processes, but there are still certain differences between the two protocols as follows:
| Feature | Ethernet/IP | Profinet |
| Base Protocol | CIP (Common Industrial Protocol) | Profinet IO |
| Vendor Ecosystem | Rockwell, Omron… | Siemens, Phoenix, Beckhoff… |
| Speed & Determinism | Good (Supports CIP Sync) | Excellent (Real-time & Isochronous) |
| Tag Addressing | Tag-based | IO-based (more configuration effort) |
| Integration | Plug & play with CIP devices | Better integration with Siemens PLCs |
In summary, both Profinet and Ethernet/IP can provide powerful communication capabilities and are the best choice for your business. The issue is that you should consider and consider your system design, region, and existing hardware ecosystem before making your choice.
Conclusion
Ethernet IP HMI systems bring a new level of connectivity, visibility, and control to industrial automation environments. With standardized communications, real-time data access, and user-friendly interfaces, Ethernet/IP makes it easier than ever to build intelligent, scalable, and efficient automation solutions.
If you are planning to upgrade or build a new automation system, consider integrating an Ethernet/IP-capable HMI for faster setup, better diagnostics, and seamless device compatibility. Contact us today for a consultation!