Distributed Control System (DCS) is an intelligent control solution that helps manage and optimize complex production processes in industries such as chemicals, oil and gas, energy, and wastewater treatment. With the ability to distribute control functions to each device, DCS ensures high precision, optimizes raw materials, and minimizes risks. This system is increasingly integrated with modern technologies such as IIoT, bringing outstanding efficiency and flexibility to businesses.
What is a Distributed Control System (DCS)?
Distributed Control System (DCS) is a control system designed to manage and optimize complex industrial processes. Unlike centralized control systems, DCS distributes control functions to related devices, helping to manage many different areas effectively.
Distributed Control System is considered the central brain of the production process. The system uses a network of sensors to collect and analyze data on the status of machines such as temperature and pressure. This data is then used to quantify the amount of material that needs to be processed by each machine at any given time. This helps businesses ensure the correct use of raw materials, saving costs.

How many types of Distributed Control System (DCS) are there?
DCS systems can be classified based on their functionality and integrated technology. Here are the 4 main classifications:
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) System: SCADA is an integral part of modern DCS systems, with the main role of monitoring and managing processes remotely. This system collects data from sensors, terminals and sends control commands to specific components.

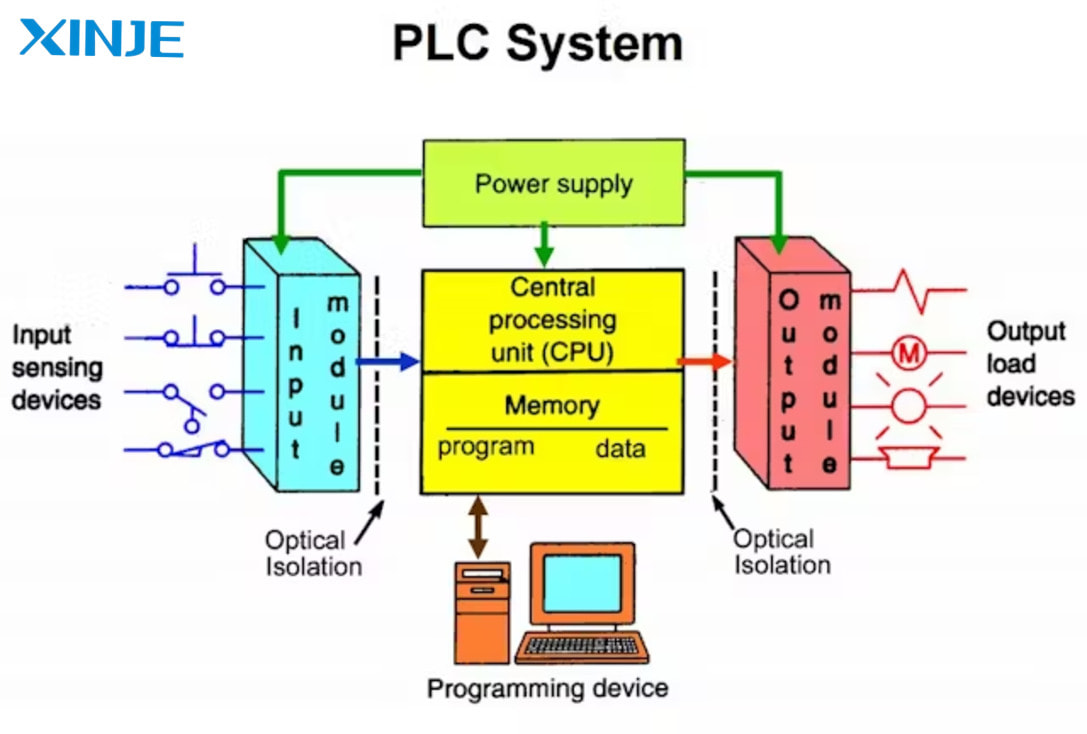
- Programmable Logic Control (PLC) System: PLC system plays a central role in DCS systems, responsible for performing automatic control tasks at specific points in the production line.

- Distributed Control Network (DCN): Distributed Control Network (DCN) is the core component that supports the connection of devices in the DCS system, helping to ensure continuous and accurate transmission of data and control commands.
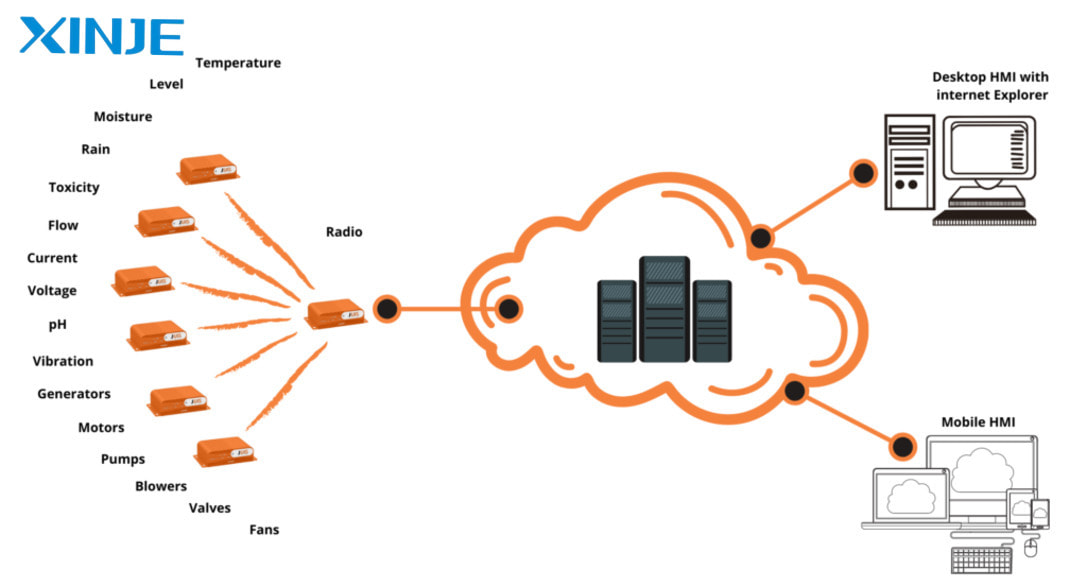
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) brings a whole new level of DCS system management and optimization by integrating modern technologies such as cloud data and intelligent analytics. IIoT connects devices and sensors in the system, allowing remote data collection and processing, and helping operators monitor and control all operations flexibly.

Thus, each type plays a separate role in ensuring automation, monitoring and optimization in production. The combination of these technologies makes DCS a comprehensive solution in modern industries.
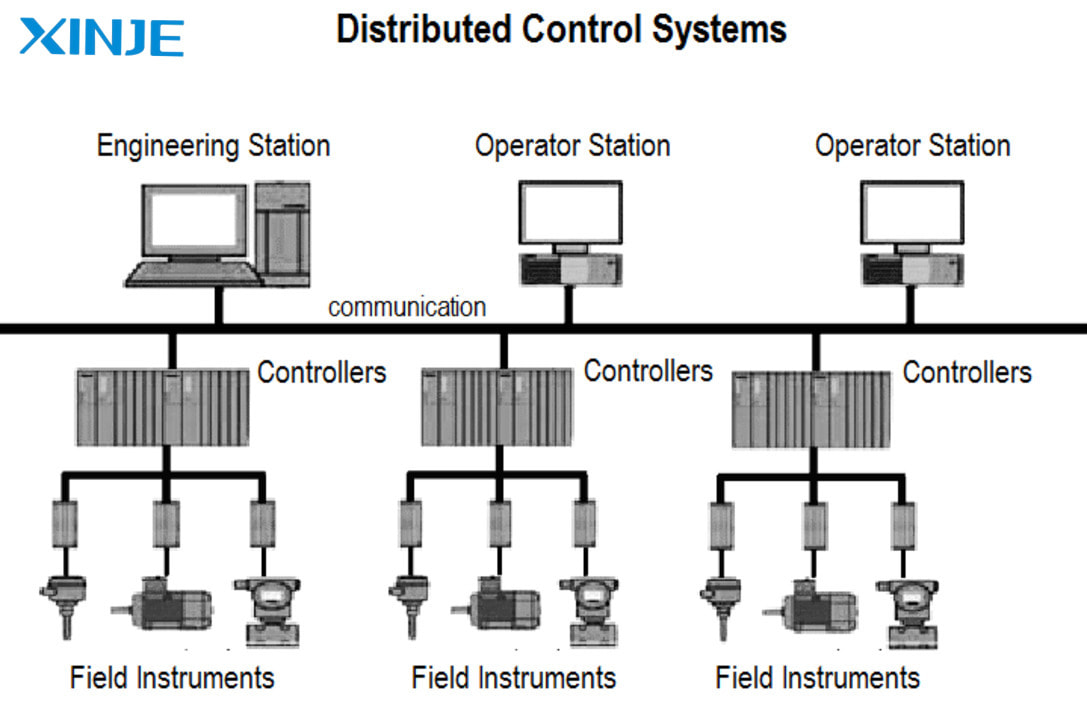
Structure of Distributed Control System (DCS)
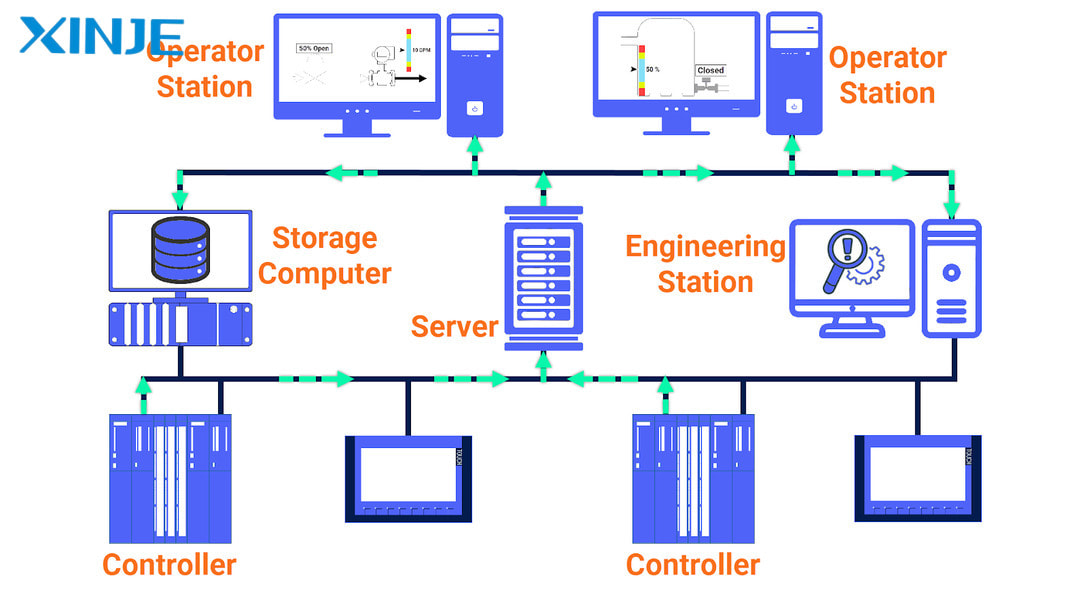
The DCS system has a distributed structure, consisting of many components connected to manage and control production processes effectively. Below are the four main components of the DCS structure:
- Local control station: Also known as the process station, it takes on the control function for a specific production stage or process. The local control station performs the function of directly controlling equipment, monitoring parameters and collecting data.
- Operator station: The operator station is where operators monitor and control the entire DCS system from the control center. Operator stations can operate independently or in parallel, and each station is usually designed to monitor a separate segment or workshop.
- Engineering station: The engineering station is where engineers configure, maintain, and optimize the DCS system. This is where software development tools are installed, allowing the creation and monitoring of application programs that control, configure, and parameterize field devices, as well as the human-machine interface (HMI).
- Communication system: The DCS communication system consists of two main parts: the field bus and the system bus.
Field bus: Connects the control station to remote I/O stations and intelligent field devices. This is the communication channel between controllers and measuring and monitoring devices in the production process.
System bus: Connects local control stations (LCS) to each other, as well as to operator and engineering stations, ensuring seamless data exchange between DCS system components.
In addition to the basic components above, a DCS system may include additional remote I/O stations, dedicated controllers, and other additional equipment depending on the specific requirements of the system and production process.

What are the benefits of a Distributed Control System?
Distributed Control Systems are the top choice in industrial automation thanks to their superior ability to control and optimize production processes. With a distributed design, this system ensures flexibility, high efficiency, and almost absolute accuracy. Here are the outstanding advantages that this system brings to businesses:
- High accuracy: DCS is designed to ensure high accuracy in controlling and monitoring production processes. This is especially important in industries that require strict control, such as chemicals or food production.
- Low error rate: Because the system distributes data collection and monitoring across many different control units, a failure in one location does not affect the entire process.
- Increased work efficiency: Advanced control algorithms in DCS continuously optimize production parameters based on actual conditions, helping to maximize productivity without wasting resources.
- Scalability: The DCS can be expanded with more control units and modules as needed.
- High flexibility and integration: The system can communicate with various protocols such as actuators, human-machine interfaces (HMI), Modbus, Profibus, and Ethernet/IP, allowing for better integration across the entire automation ecosystem.


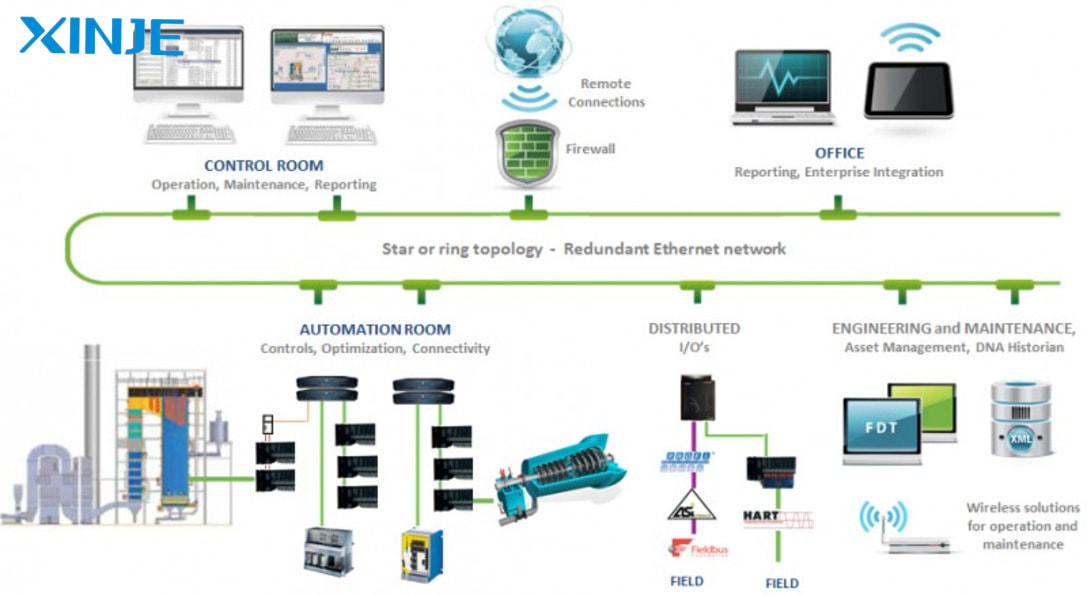
In which industries are Distributed Control Systems (DCS) commonly applied?
- Process Industry: DCS helps monitor continuous manufacturing processes in industries such as chemicals, oil and gas, food, and pharmaceuticals, where precise control of variables such as temperature, pressure and flow is critical.
- Chemical Industry: DCS controls processes such as mixing, reacting and separating in chemical manufacturing. With hazardous materials, DCS reliability is critical to optimizing production, reducing waste and saving energy.
- Oil and Gas Industry: DCS is used to monitor and control operations from upstream to downstream. From drilling and oil and gas production to pipeline monitoring and storage, DCS ensures these processes are safe and efficient.
- Nuclear Power Plants: DCS systems manage complex processes such as nuclear fission, temperature and pressure control in the reactor, ensuring plant safety.
- Wastewater Treatment: DCS treats and removes pollutants from wastewater to meet environmental protection standards and protect the ecosystem.

Conclusion
Distributed Control System (DCS) is not only a production management tool but also a key factor to help businesses achieve high efficiency and minimize risks. With precise control capabilities, scalability and advanced technology integration, DCS will certainly continue to be the leading trend in the field of industrial automation.