The Servo motor is a specialized device used to control the movement of the device most accurately. The device is usually operated by generating torque and velocity according to the command from the controller.


This servo motor includes two main classifications with many outstanding features, can handle quickly and respond to problems in many different problems, widely used in many modern industries such as fast assembly robots, packaging and production speed, and control of electronic devices…
Possessing many outstanding features and diverse price segments, servo motors are rotation control devices that every industrial facility should own.
Are servo motors expensive or cheap?


How much does a servo motor cost? Many users are interested in this question. However, it is difficult to have an exact answer to the price of a device. For example, some types of servos with low prices will not operate optimally and they are often made from components with short life spans. In addition, more expensive servo motors are often elaborately manufactured from potentiometers with quality control circuits and can operate stably in the long term and meet many criteria for the operator.
Therefore, the price of a servo motor depends on the operating capacity and structure of the device. But in general, the cost of each servo motor will fluctuate in the price range of $100 – $1,000.
What are servo motors commonly used for?
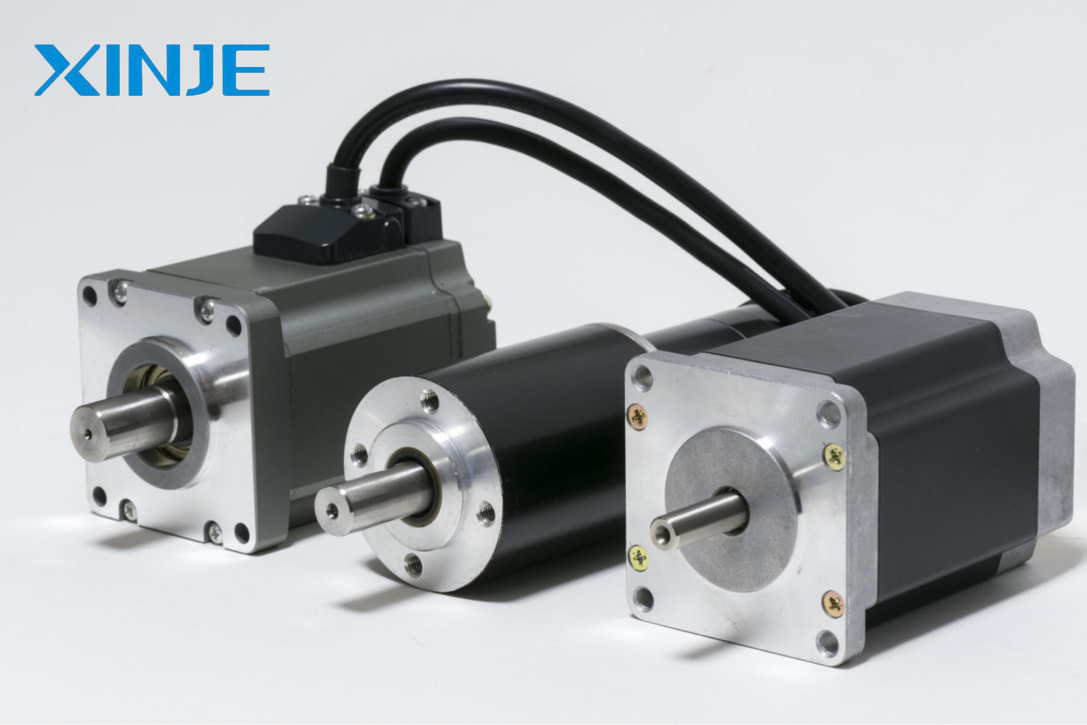

Servo motors are modern motion control devices and have diverse applications in many different automation industries such as:
- Industrial robots: Servos support robots to control arms and grippers with high precision and smooth movements. These robots are popular for tasks such as assembly, welding, and material handling.
- Automatic CNC machines: Servo motors will ensure the precise movement of cutting tools, speed alignment, and precise process control, bringing superior quality and productivity.
- Manufacturing – packaging industry: equipment used in conveyor lines, packaging machines, and printers, providing precise control, improving operational efficiency, and reducing downtime in the process.
- Control of electronic devices: Servos support devices such as cameras, supporting autofocus, and image stabilization, and consumer products such as DVD players or home automation systems.
- Renewable Energy: Servo helps optimize and precisely determine the position of solar panels in tracking systems, increasing energy collection efficiency.
How does the servo motor work?
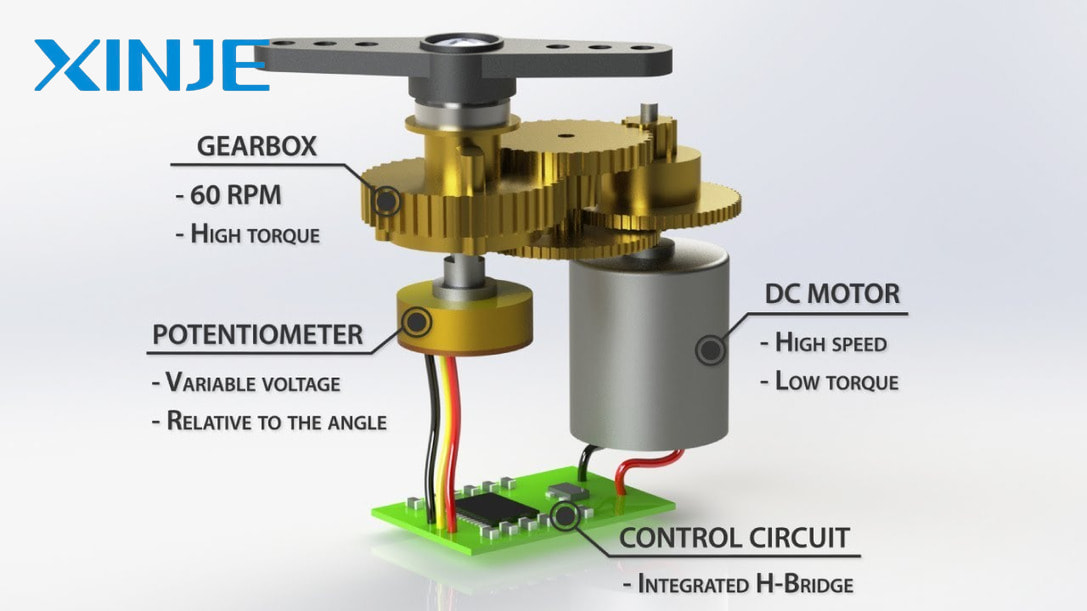

Servo motors operate by generating torque and velocity according to commands from the controller, operating in a closed-loop system. The feedback device provides position, velocity, or current information to the controller to adjust the motor operation precisely.
Servo motors operate based on pulse width modulation (PWM) signals. This signal determines the position of the servo shaft, with a 1.5ms pulse usually returning the shaft to neutral (90°). Shorter or longer pulses will control the shaft to rotate to 0° or 180°. When commanded to move, the servo will rotate to the desired position and hold that position. If acted upon by an external force, the servo will counteract this force to maintain a stable position, based on its torque rating. To keep the shaft at a certain position, the PWM signal must be sent continuously every 20ms.
When users clearly understand the process and operating principles of servo, it will help them easily choose the right device that meets the set criteria.
What are the classifications of servo motors?
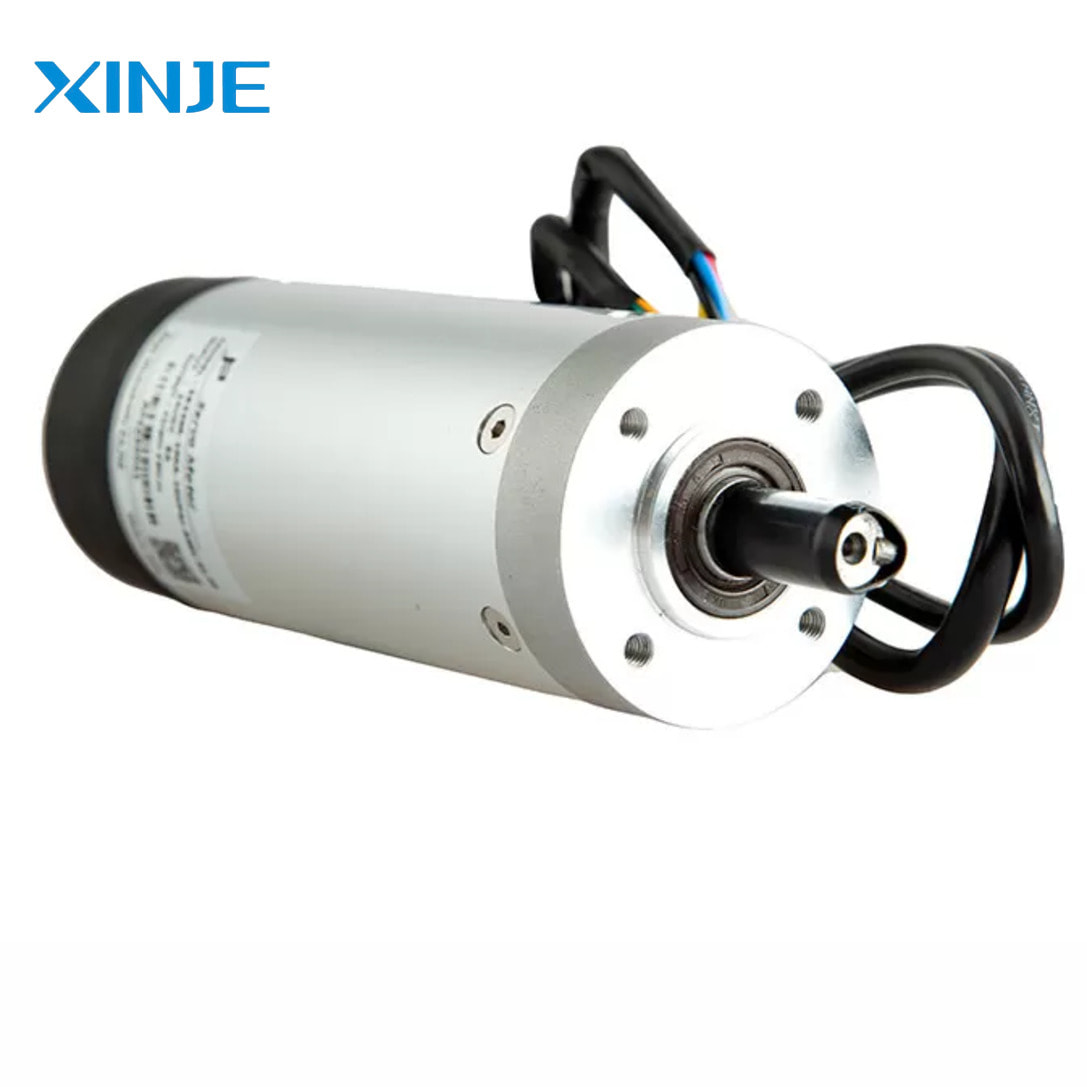
DC Servo Motor
DC servo motor consists of a position sensor, gear assembly, and control circuit. The device helps to precisely control the speed and position of an object through a reference DC voltage. In addition, it also uses feedback from the sensor to adjust the mechanical position, ensuring high precision, and is widely used in systems requiring high precision such as production lines, packaging, assembly, etc.


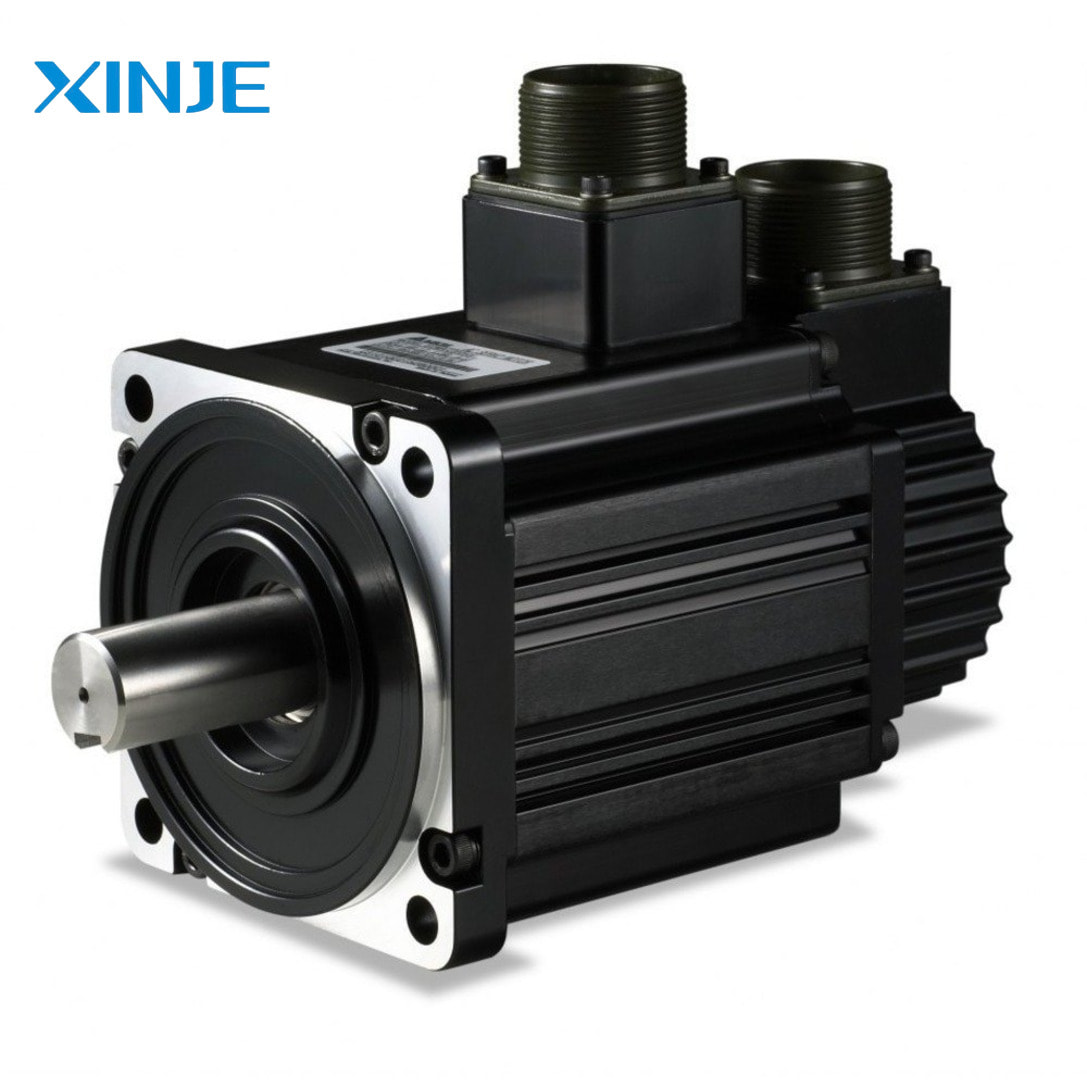
AC Servo Motor
This is a two-phase induction motor, specializing in converting AC power into precise mechanical motion. The device usually operates in a power range from a few watts to several hundred watts, with a frequency of 50–400 Hz. In addition, it also integrates an encoder to track speed and position, providing superior control and precision. Very suitable for industrial applications requiring advanced feedback systems.


What are the advantages and disadvantages of servo motors?
Advantages
- Comprehensive control and monitoring: Servo motors are capable of controlling objects at a certain position and speed, with high precision, the device is suitable for applications with repetitive steps and high stability.
- High torque: Maintain torque at all speeds, even at low speeds, well responding to tasks requiring large capacity and high precision.
- Fast – timely response: Servo motors are capable of quickly adjusting to changes in load, speed, or position, ensuring continuous system performance.
- Smooth operation – long life: The device helps reduce vibration, minimize wear and tear, and bring stability to the entire system thanks to its durable design and long-term operating life.
- Energy saving: The device helps optimize power consumption, reducing operating costs over the long term.
Disadvantages
In addition to the outstanding advantages that servo motors bring, the device still has certain limitations during use that users need to pay attention to:
- Complex control system: Servo motors require complex control and feedback mechanisms, increasing the difficulty in design, and requiring highly skilled operators to monitor and manage.
- High cost: Servo motors are applied with many advanced features and precise control capabilities. Therefore, they are often more expensive than conventional motors.
High heat generation: During operation, servo motors generate significant heat, requiring additional cooling systems to avoid overheating and ensure stable performance.






