SCADA is a system that is often used in combination with PLCs and other devices in the process. They can be pre-programmed software on the computer or can be a human-machine interface or HMI.


Besides that, this device is also used for monitoring, controlling, and collecting data for large-scale industrial plants such as manufacturing plants, power plants, or water treatment industrial parks…
Thanks to the application of advanced and modern technologies such as remote access, data analysis, and general integration with other systems such as MES, ERP, DCS, etc., the SCADA system will help monitor and collect data for the entire process more accurately and effectively.
What are the components of SCADA?
A complete SCADA system is made up of many different components including hardware and software. Some basic components in each SCADA system are:
- Sensors and actuators: these parts help measure industrial process parameters such as temperature, and pressure. In addition, they also help control devices such as valves and switches during system operation.
- RTU and PLC conversion units help collect data from sensors and transmit it to the main system based on data collected from RTU and process standards.
- The monitoring computer will help control and collect data from field devices at the conversion unit, and send control commands to the operator to control the entire process.
- HMI software: supports data presentation from PLC and RTU conversion units, allowing operators to monitor and adjust all activities in the system.
- Communications infrastructure: enables SCADA systems to communicate with field devices and controllers, ensuring accurate data collection and control.
How many types of SCADA are there?
SCADA systems are divided into four main types: Monolithic, Distributed, Networked, and IoT Integrated. Each type will have different characteristics and operating processes.
- Monolithic SCADA is a device that operates independently of other devices. They are often processed and controlled in a large computer, most suitable for industries that require high control capabilities but have limited flexibility and scalability.
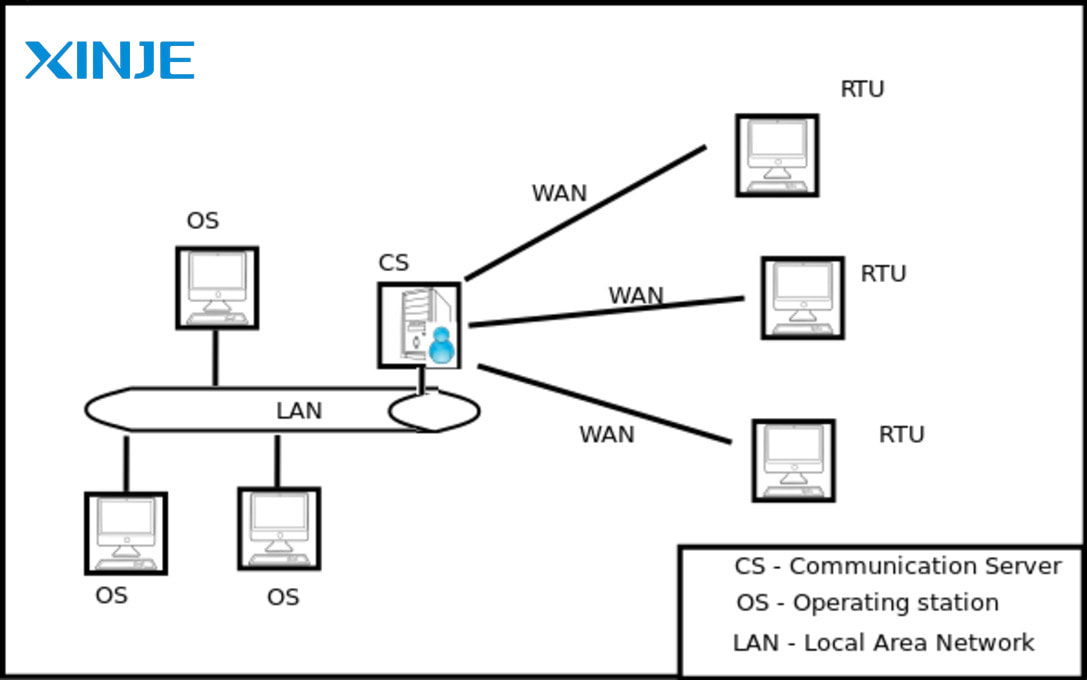

- Distributed SCADA is evenly distributed among many nodes, making the system more flexible and easier to connect and expand. These nodes can communicate and coordinate with each other, improving system availability and safety.
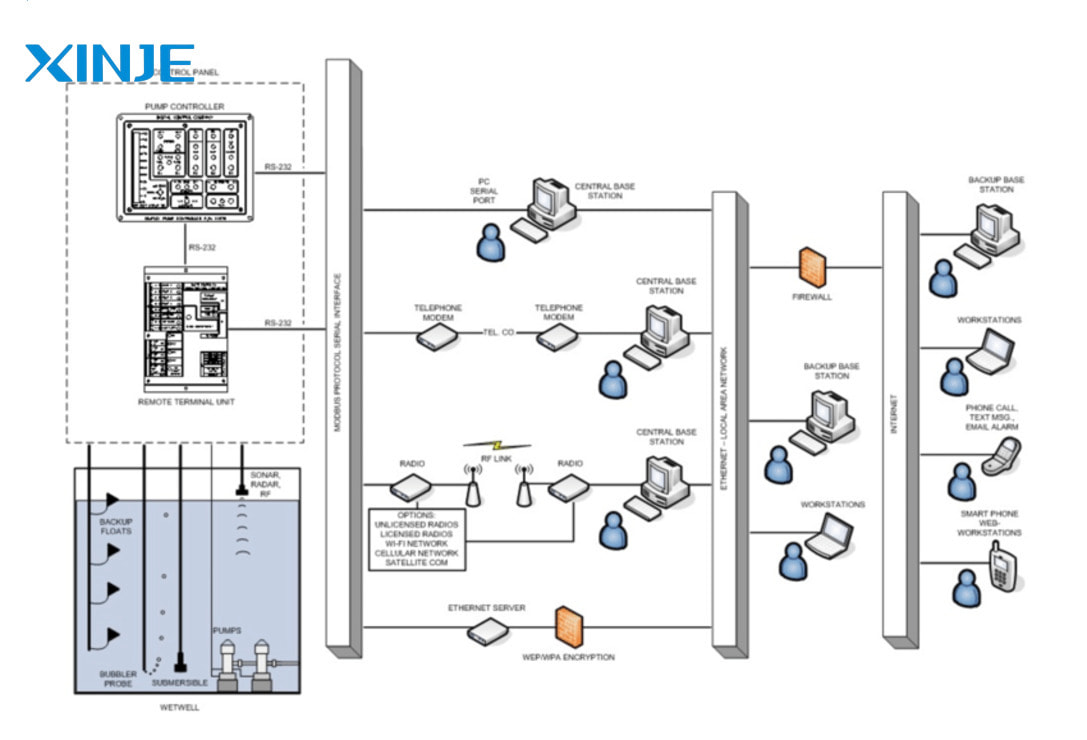

- Networked SCADA allows the connection of multiple SCADA systems in different locations, enhancing the ability to monitor and control from a single center, widely applied in places such as power grids or oil and gas.
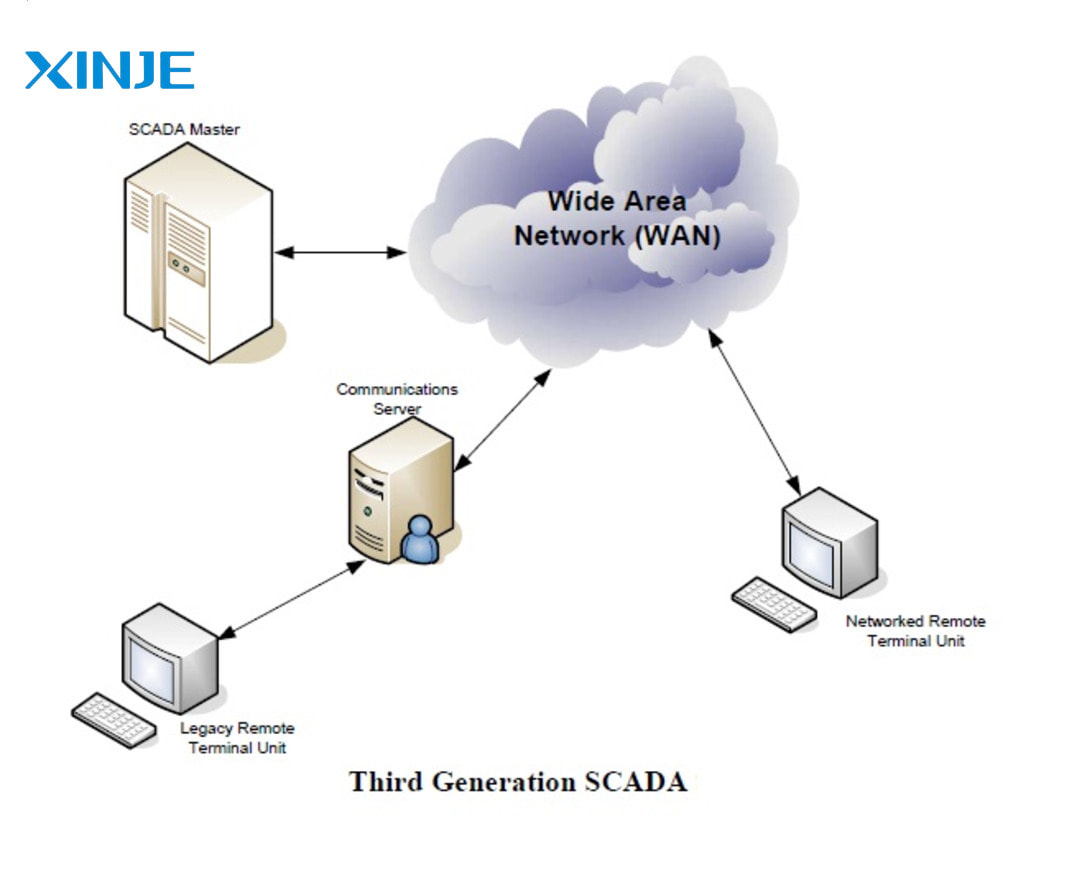

- SCADA Integrated IoT is connected to sensors and devices via the internet, supporting the collection and analysis of big data from the field thanks to the ability to monitor, control, and accurately predict equipment failures.
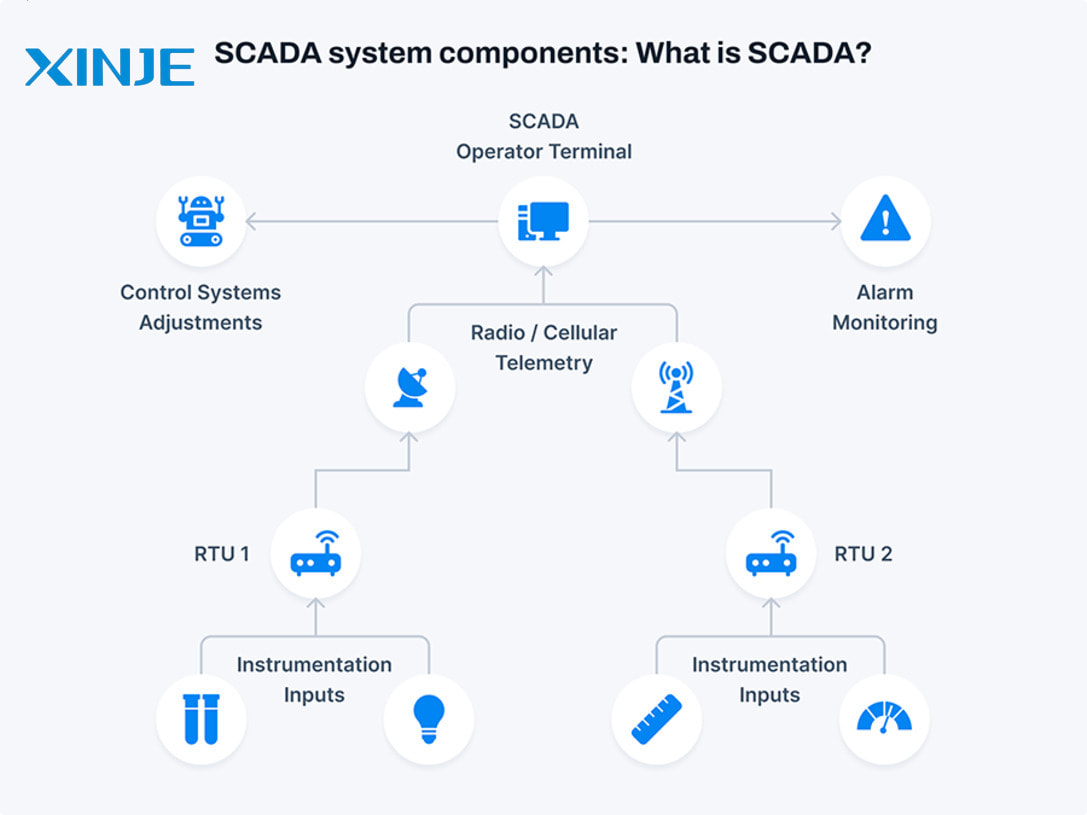

What is the role of SCADA in automation?
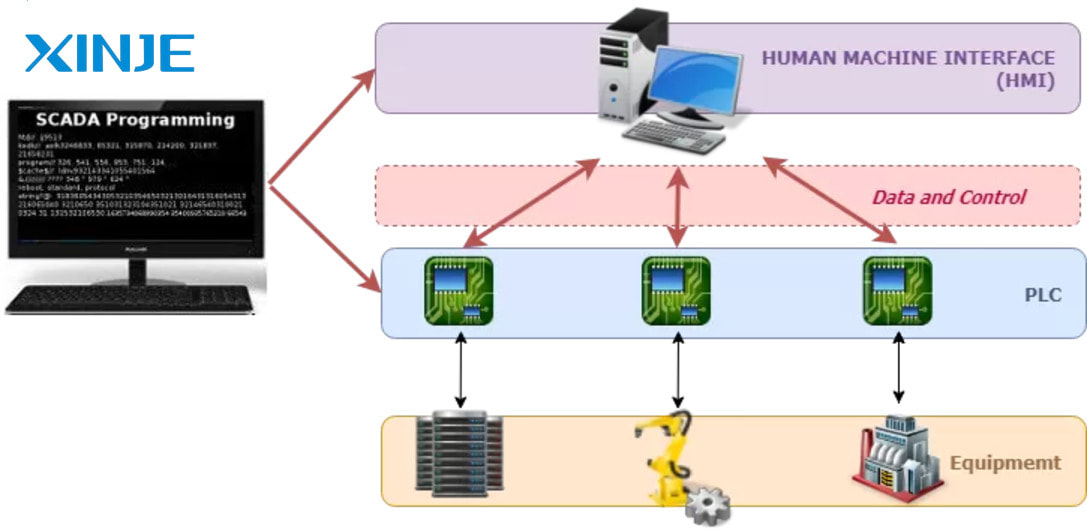

SCADA is a device that has helped many control processes of many automation systems become more efficient. In addition, other outstanding functions of this system are worth noting such as:
- Data collection: SCADA supports the collection of information from sensors and measuring devices such as temperature, pressure, speed, and weight. Then convert the data into easy-to-understand information for operators.
- Control: SCADA systems can control processes automatically from power on/off, to speed adjustment based on collected parameters.
- Alarm: SCADA can emit warning signals such as lights and sounds when problems occur to easily notify operators quickly and help them classify the priority of the problems.
- Data communication: SCADA uses communication protocols (DNP3, Modbus, IEC 60870-5) to transmit data between machines and operators over wired or wireless networks.
Where is SCADA commonly used?


SCADA systems are highly reliable monitoring devices and are widely used in many control and automation industries to help reduce downtime in the process and improve overall system efficiency. Some typical applications of SCADA include:
- Oil and gas industry: SCADA helps monitor and remotely control operations such as pumps, rigs, and refineries located in remote locations, ensuring timely data distribution and effective decision-making.
- Transportation industry: SCADA is integrated into traffic light control and public transport monitoring, ensuring smooth traffic flow and minimizing congestion.
- Water and wastewater management: SCADA monitors water flow, pressure, and water levels in water supply and wastewater treatment systems, especially in remote locations.
- Energy management: SCADA helps monitor and control the power grid, circuit breakers, and electrical systems at power companies, easily detect remote incidents, and ensure continuous and timely power supply to households.
- Manufacturing industry: SCADA will control and monitor all activities in the production and automation process, easily detect errors in the process, and monitor system operations in remote areas.
What are the differences between PLC and SCADA?


PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) are both important programming systems in large manufacturing processes. But there are still many people who easily confuse these two systems, so below is a detailed comparison table between PLC and SCADA.
| PLC | SCADA |
| PLC focuses more on control programming capabilities | SCADA focuses heavily on displaying, controlling, monitoring, and collecting data. |
| PLC will include input/output modules and a CPU central processor to control the program. | SCADA does not have input and output modules, but it will have remote terminal unit RTU |
| PLCs are often programmed in a variety of other languages such as ladder language, structured text, and command lists… | SCADA uses a specialized scripting language to monitor and alert the process if an error occurs. |
| PLC is popular for discrete products. | Applicable to any control process whether discrete or integrated, as long as the control process system has data collection. |
| PLC has a compact, simple, and sturdy structure. | SCADA is software installed on industrial computers or specialized PCs to manage and monitor operating processes. |
| PLC is the most suitable solution for small and medium-sized businesses. | SCADA is suitable for small to large scale, mainly large scale with complex systems and higher requirements. |
| PLC is more specialized for controlling and optimizing production processes. | SCADA is used by engineers to know the current state of the plant process. |





