A programmable logic controller (PLC) is a rugged industrial-grade digital computer used to control machines and processes in manufacturing environments. Designed to withstand harsh conditions such as vibration, humidity, and electrical noise, PLCs are an essential part of manufacturing automation and assembly lines, robotic equipment, or conveyor systems.
A human machine interface (HMI) is a user interface that connects an operator to the controller (e.g., PLC) of a machine or system. This interface provides a visual representation of the control system through a control panel, touch screen, or graphical display. Therefore, combining and exchanging data between these two devices is essential. Follow this article to find out how HMI and PLC will exchange data.
How to integrate PLC and HMI?

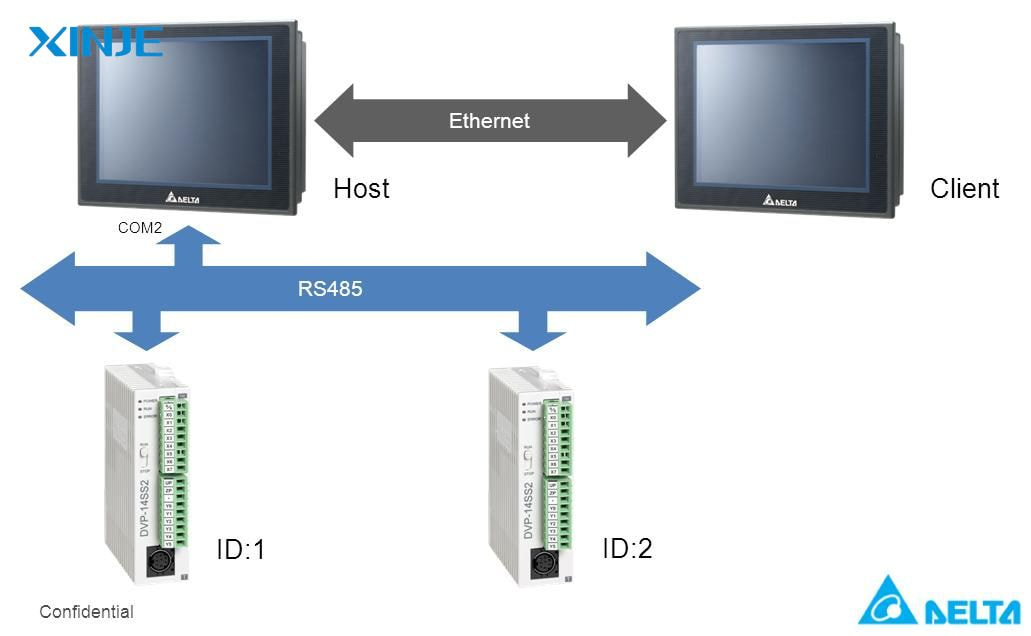
To enable PLC data exchange with HMI, you need to establish a reliable communication channel between the two systems. This integration involves selecting the appropriate hardware, selecting a compatible communication protocol, and programming both devices to transmit data synchronously.
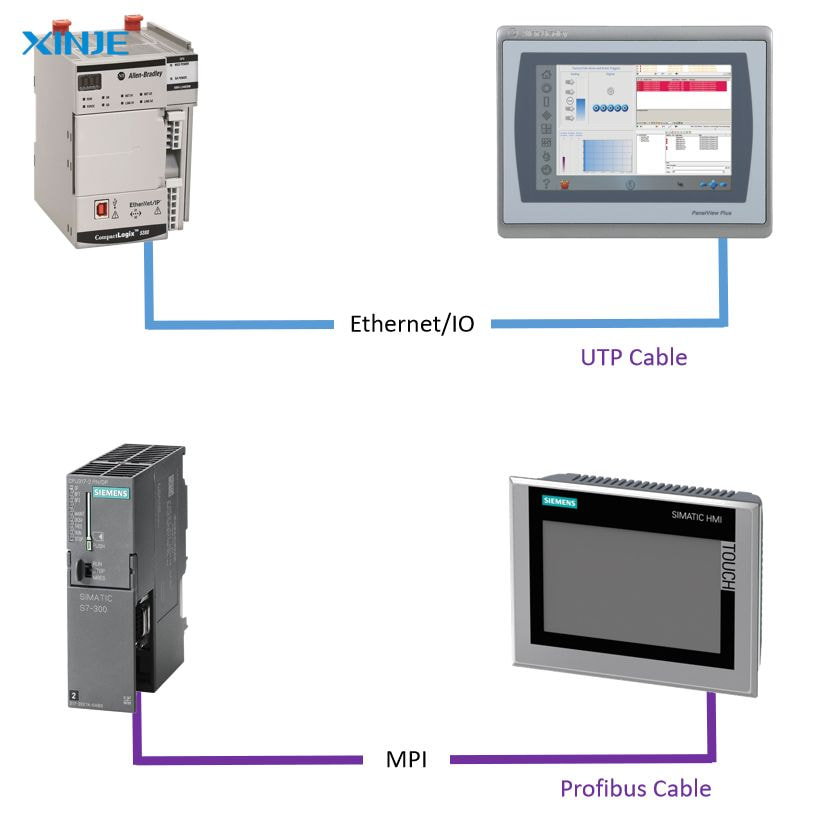
- Choose the right communication protocol: The protocol determines how data is transmitted between the PLC and HMI. Common communication protocols include: Modbus, Ethernet/IP, Profibus, Profinet, or OPC UA…
- Configuring IP Addresses and Network Settings: If you are using Ethernet-based communication, assigning static IP addresses to both devices will ensure consistent connectivity so that the port and baud rate must be properly matched.
- Tag Mapping: Tags are variables that store real-time data in the PLC. These tags must be properly mapped in the HMI to display or control process values.PLC and HMI Programming
- In PLC programming software, the logic and tag assignment are defined. In the HMI software, the interface, gauges, charts, and input buttons will be designed and linked to the PLC card.
- Testing and troubleshooting: Before going into operation, check the integration for some issues, such as whether the data is transmitted correctly. Can the operator write to the PLC from the HMI? Are the alarms and logs displayed as expected? etc.
What are the benefits of exchanging data between HMI and PLC?
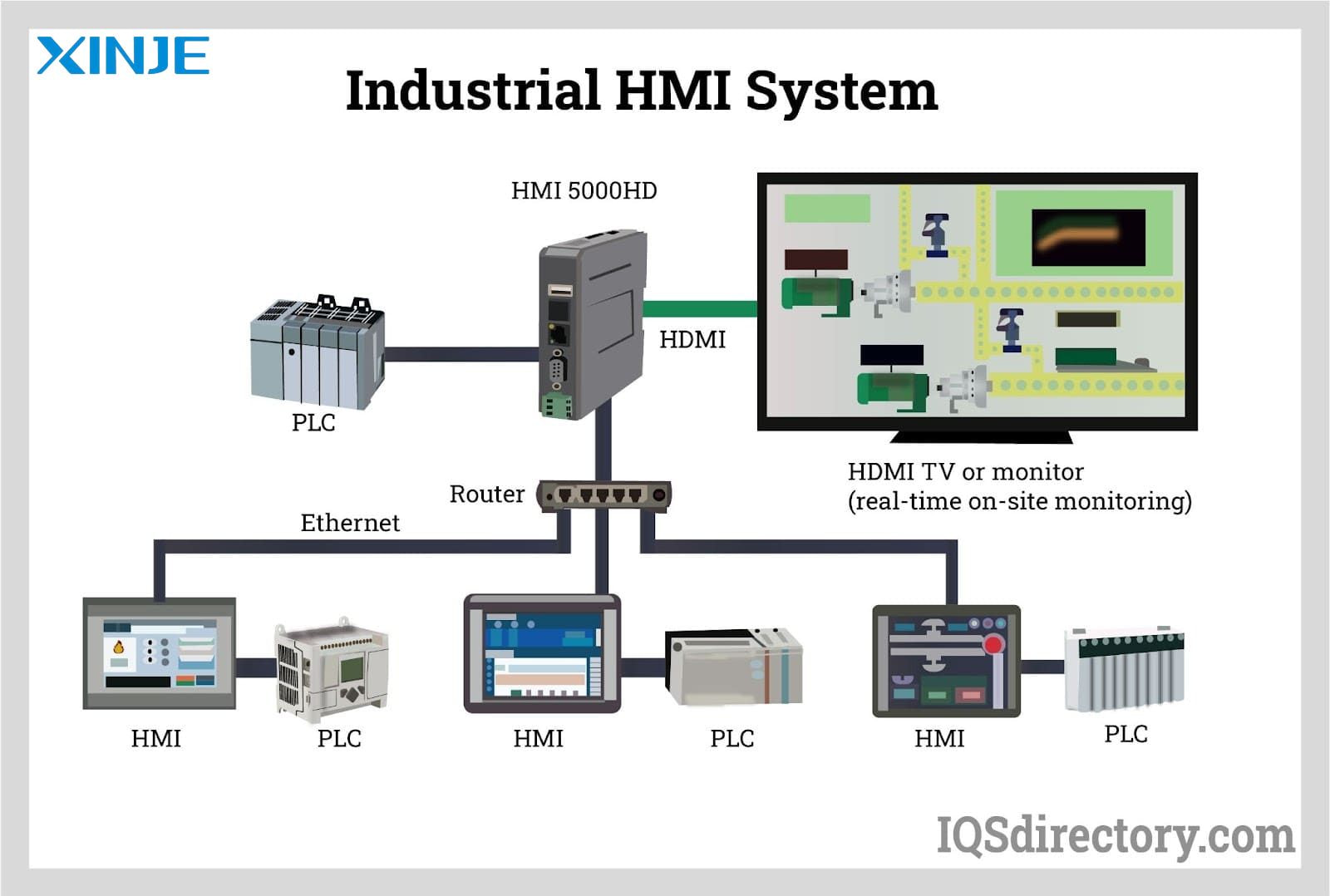

Seamlessly combining and exchanging PLC data to HMIs offers many advantages that increase industrial performance, efficiency, and safety.
- Real-time monitoring: Operators can visualize process variables in real time, such as temperature, speed, or voltage. This makes decisions faster and ensures the system operates within desired limits.
- Improved control and flexibility: Instead of manually adjusting settings at the machine, operators can use the HMI to modify process parameters, which is extremely useful for large-scale systems or remote locations.
- Alarm management: Critical issues such as overheating or mechanical faults can be flagged immediately via the HMI interface. Visual and audible alarms help operators react quickly, minimizing downtime.
- User access control: User access levels can be defined via the HMI screen. For example, only supervisors can access certain control functions or reset alarms, which improves system security.
- Minimize human error: By replacing manual controls with a graphical interface, the possibility of operator error is reduced, especially when using preset values and ranges.
What problems can occur when exchanging data between the PLC and HMI?
There are many benefits to integrating HMIs and PLCs into an automation process. However, some challenges can arise. Certain challenges can still arise when exchanging data from the PLC to the HMI:
- Loss of connection: If the cable is loose or the IP configuration is incorrect, the HMI may not be able to read or write data to the PLC.
- Mistaken tags: A common problem is inconsistent tag names or address configurations between the PLC and HMI, which can result in blank data fields or faulty control.
- Protocol incompatibility: Some PLCs and HMIs may not support the same protocol, especially if they are from different vendors. In such cases, a protocol converter or OPC UA gateway may be required.
- Unauthorized access: If the HMI is connected to a larger network, the cybersecurity risk increases. Firewalls then authenticate users, and encrypted protocols like OPC UA help mitigate threats.
Conclusion
PLC and HMI integration is the foundation of intelligent, responsive, and efficient industrial automation. When done right, PLC and HMI data exchange enables real-time control, better decision making, and improved system safety.
From choosing the right communication protocol to ensuring accurate tag mapping and secure data transfer, every step plays a vital role in optimizing system performance. At the same time, being aware of potential pitfalls from connectivity issues to version mismatches helps ensure smoother operations and less downtime.