Human-Machine Interface also known as HMI, is a technology system that helps operators control, monitor, and diagnose errors when operating machinery. They are often widely used in large industrial processes and industrial zones that require high automation.
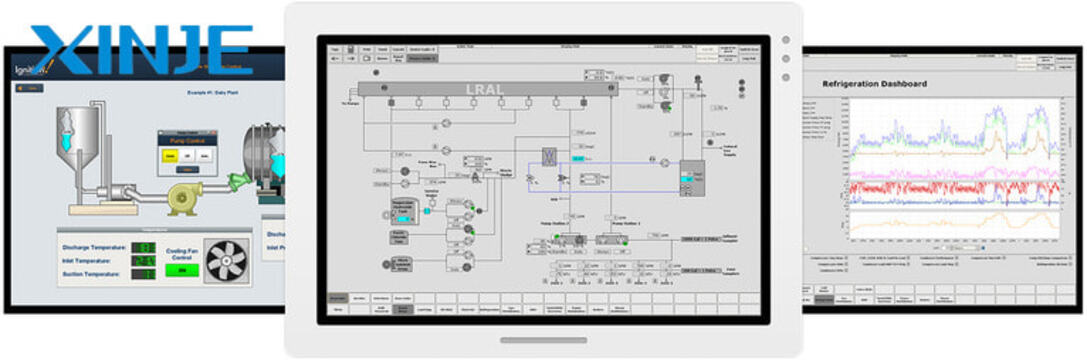

HMI has many different classifications such as Operator, Touch screen, and Physical control panel. Each classification will have different functions and components. But in general, the HMI system is still a perfect choice in the current 4.0 era, helping to optimize many production processes, provide timely information on performance, or promptly notify errors that arise in the machine during operation.
What components does HMI include?
HMI (Human Machine Interface) comprises components such as PLC, Control Systems, Software Applications, Inputs, and Outputs.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): PLC systems help automate the entire process from small to large scale, helping to control and monitor the stages. In addition, this part is considered the brain of the chain, executing and issuing pre-set general commands, ensuring that the entire operation process runs smoothly and brings high efficiency.
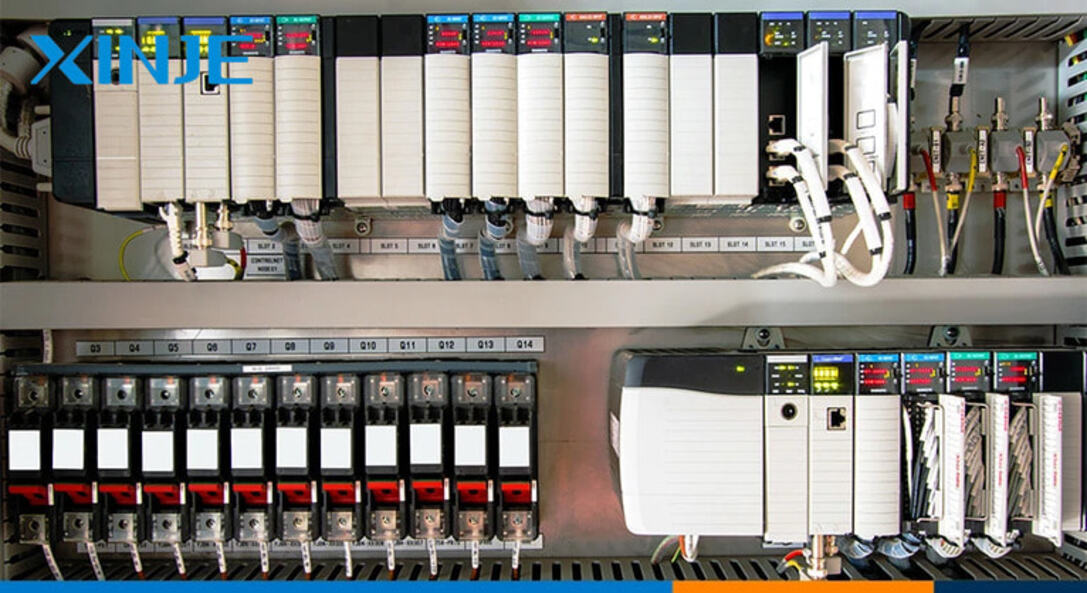


- Control Systems: In HMI, the control system is set up in a more advanced way because it integrates many additional features such as sensors, management, adjustment of process behavior, machinery, etc. Moreover, the structure of this part is also quite complex, they operate by using algorithms and specialized feedback loops to build commands in the process to help all operations stabilize and achieve the best performance.

- Software Applications: This application will provide many smart features such as data visualization, real-time monitoring, alarm management, and diagnosis… to help operators easily interact and effectively manage the entire system.
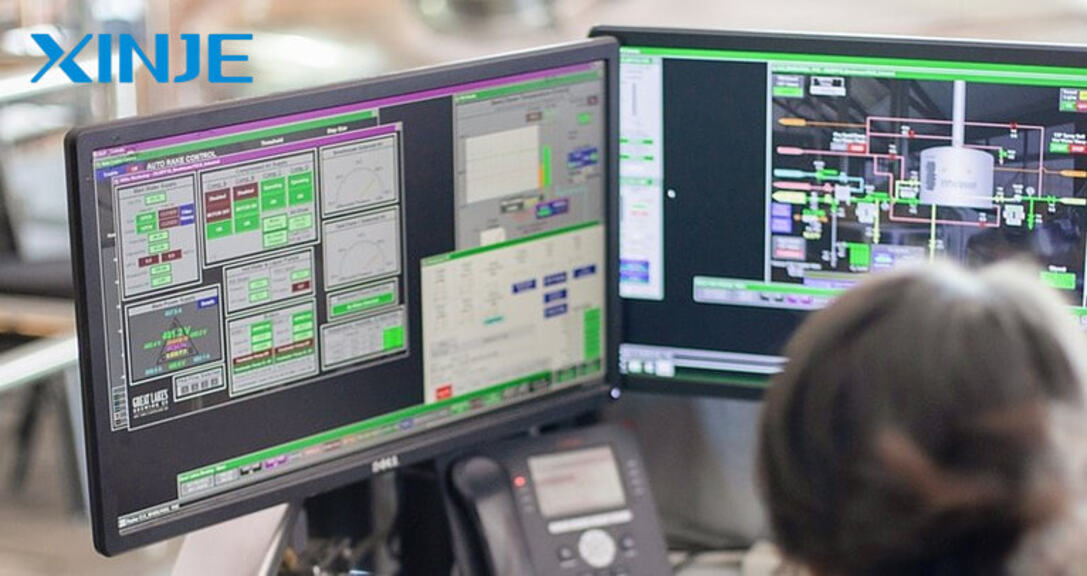


- Inputs and Outputs: Thanks to the I/O input and output components, data exchange between users and machines becomes much more convenient, and operators will easily recognize signals from the computer when a problem occurs. For input, there will be a keyboard and touch screen. As for output, there will be an LED screen and a monitor.


What types of HMI are there in the industry?
HMI Human Machine Interface includes many classifications in different formats, such as machine screens, computer screens, smart devices, etc. Regardless of the classification, the ultimate purpose of HMI is to provide information about the production process to the operator, ensuring high efficiency and stable operation.
HMI has 3 basic types:
Operator
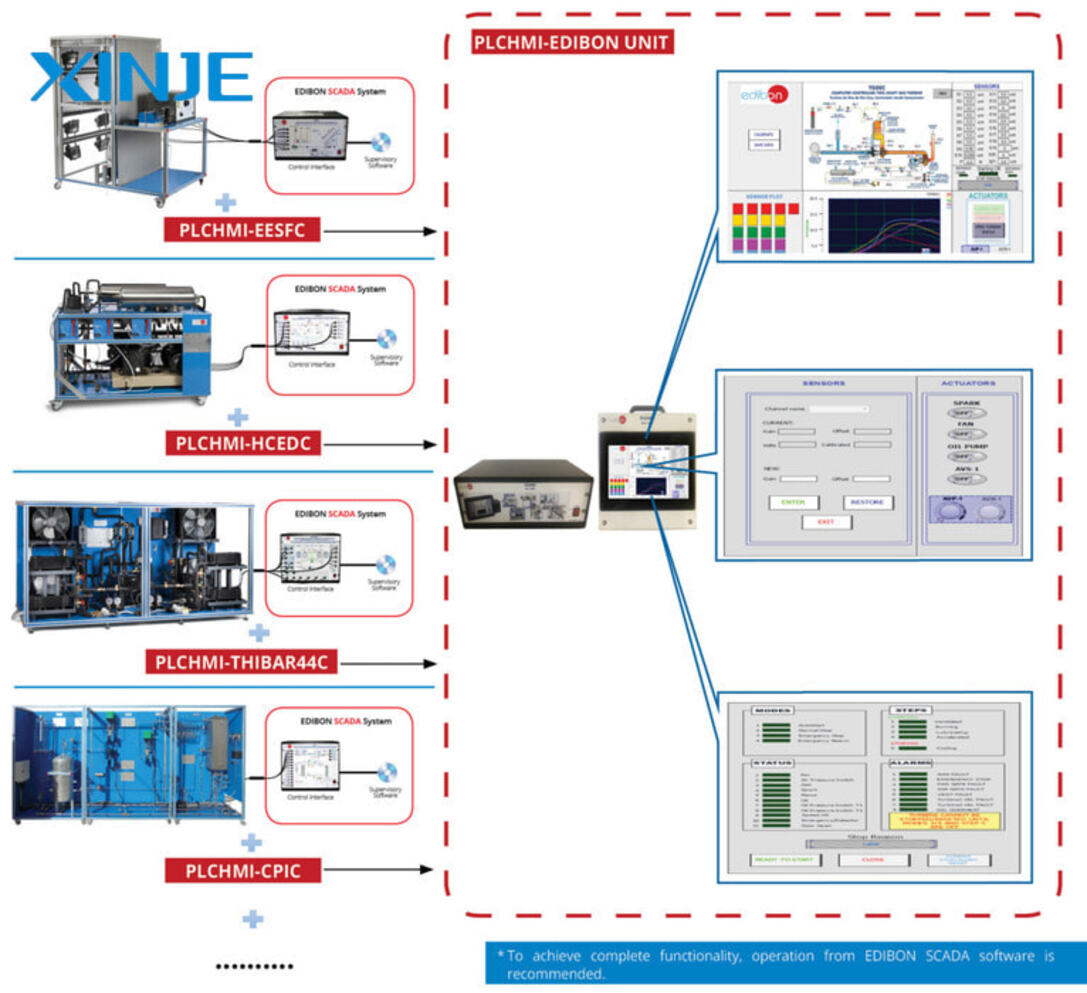
HMI monitoring will benefit the process because they have some applications related to SCADA and MES, considered the most effective centralized monitoring system for the entire site or complex of the whole process. In addition, HMI linked to SCADA also helps manage, diagnose, and provide trend data, assisting the operation process in optimizing and being most efficient.


Touch screen
For the touch screen classification, HMI allows the operator to operate and enter commands directly on the touch screen. Through these commands, the administrator can understand the machine’s graphics, and easily control and monitor the entire operation. Notably, this is a classification that is highly appreciated for its convenience and efficiency because the user only needs to touch and operate the menu directly on the screen.


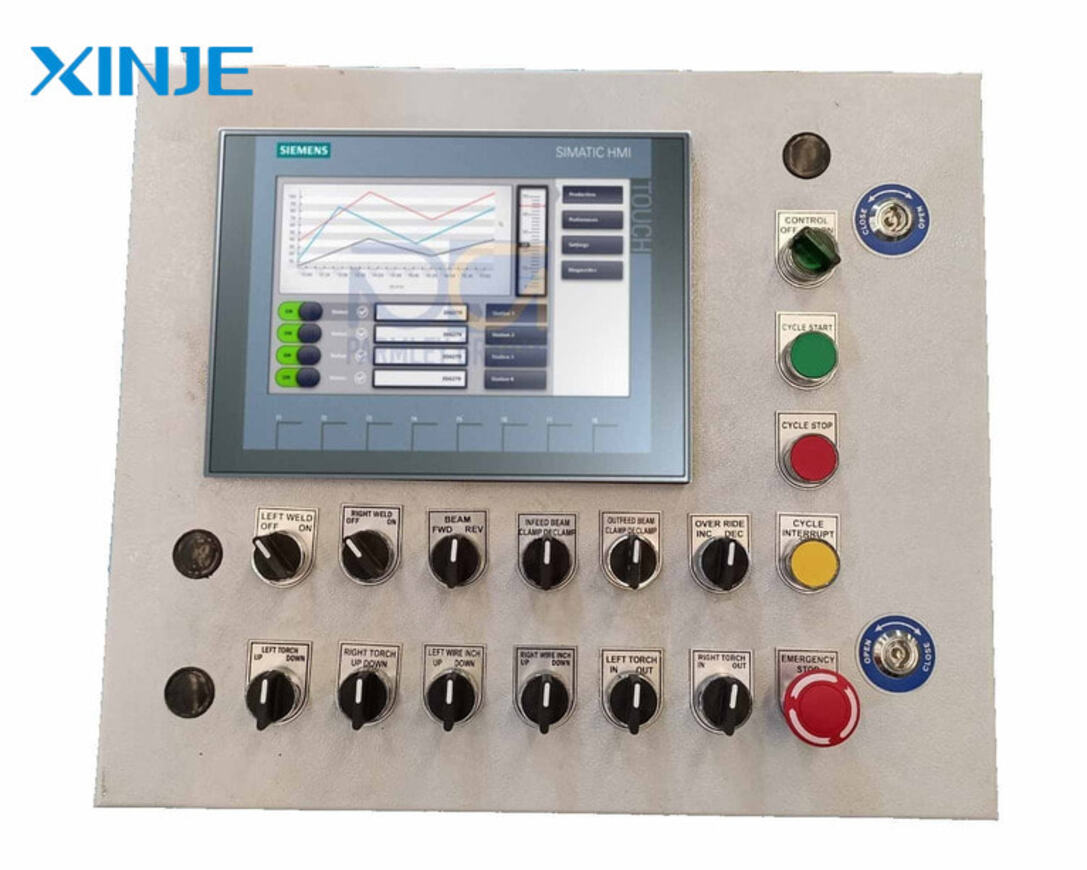
Physical control panel
In contrast to the touch screen, the physical control panel type operates based on the use of buttons, screens, and switches so that the operator can display data manually through those physical buttons. This classification is often widely used in high-vibration environments.


What are the advantages and disadvantages of HMI?
Advantages
- Easy to Use: the system has a user-friendly design, suitable for many people, even new technicians can easily access and monitor industrial processes.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: HMI allows technicians to operate and monitor the entire system remotely without any obstacles, this is a great advantage of the system and becomes useful for processes located in dangerous and remote places.
- Improved Efficiency and Increased Safety: almost all information about the process has been installed and displayed on the screen, so it is easy for supervisors to access and check very conveniently, they will easily detect and check errors in time, easily solve potential problems as soon as any issue occurs in the process.
Disadvantages
- Additional costs: the application of HMI systems in the production process can cost a significant amount of investment for businesses, because they, like other types of hardware and software, require careful investment and quality to ensure the process is operated stably.
- Users are dependent on HMI: in cases where HMI is faulty or unavailable, users will not be able to access the system to enter commands for the operating process, hindering the progress of the process being monitored.
- Potential for human error: some basic errors that users are likely to make when using the HMI system are entering incorrect commands, and not noticing alarms from the system when there is an error… this will also affect the progress and control process of technicians in the process.
In general, HMI is like many other types of industrial automation systems, each will have its advantages and disadvantages, besides the advantages and conveniences they bring, there are still disadvantages. As long as you can optimize and minimize those disadvantages, HMI is still a modern system that every industrial automation process should own.
In what fields is HMI commonly used?
HMI systems are chosen and used by many industrial organizations to improve efficiency, and safety and optimize their production processes.
Some industries that often apply HMI technology significantly include:
- Aerospace industry: HMI systems are used for air-conditioning, heating, and guide pilots in the cockpit through screens, control panels, and navigation systems.
- Oil and gas: HMI is responsible for oil production and refining processes as well as pumping, drilling, and filling oil.
- Water treatment plants: HMI is applied to waste treatment industrial parks to help coordinate and control automatic pumping and water treatment processes.
- Power generation: HMI is commonly used in fossil fuel plants or renewable energy plants to operate and manage many processes such as turbine control, electricity generation, and distribution to residential areas.
- Bank: The HMI system applied at ATMs helps customers’ transactions such as withdrawing money, checking balance, and exchanging money… take place safely, quickly, and conveniently.
The Role of HMI in Industry 4.0
Along with the era of 4.0 technology, the HMI system is gradually becoming a type of smart manufacturing technology and ensuring many important roles such as creating intelligent links between users and machines, automatically evaluating data, and improving more modern automation processes.
Some improvements in HMI are developed by IOT and industry 4.0 developers.
Voice recognition interface: this version allows access and input control without using the touch screen, we operate based on questions and commands set by voice, this version is a step forward in the process of greater progress for remote operation.
Gesture interface: The gesture interface allows to operation of the process without information through touch icons from hands or heads. We operate through algorithms and conversion settings so that the device can communicate with users faster and more accurately.
VR & AR tools: VR tools support the simulation of the environment like virtual reality, creating a skill teaching environment, helping technicians to identify problems and be able to repair them. AR tools will provide more technical information about specific conditions accurately.
HMI in the 4.0 era promises to be an advanced technology system, with outstanding working performance and bringing many benefits in the most intuitive and standardized way to the production process. HMI can be seen as the golden key to optimizing many automatic processes in this 4.0 era.
How do you choose the right HMI?
Some factors you need to consider when choosing an HMI system for your business.
Scalability: HMIs that are scalable and can handle complex process tasks effectively are considered a plus and should be chosen for your business.
Data visualization: you should prioritize choosing HMIs that can display data clearly, and consistently and use a variety of expressions such as graphics, charts, or other visual representations as long as they help operators access easily and make the right decisions.
Compatibility: you should consider choosing HMIs that are compatible with the system they will control. In addition, compatibility with the communication protocol and data format that the HMI uses should also be considered.
Cost: Prioritize choosing a quality HMI but don’t forget the cost issue, you still need to consider your current budget to choose a suitable HMI.





