Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is increasingly widely used in modern factories thanks to its comprehensive production monitoring and management capabilities. From real-time data collection, process optimization, quality control, and waste reduction, MES has become a powerful tool for businesses. But is this system suitable for all types of production? Let’s explore the benefits, challenges and possibilities of integrating MES with ERP in detail in this article!
What is a Manufacturing Execution System (MES)?
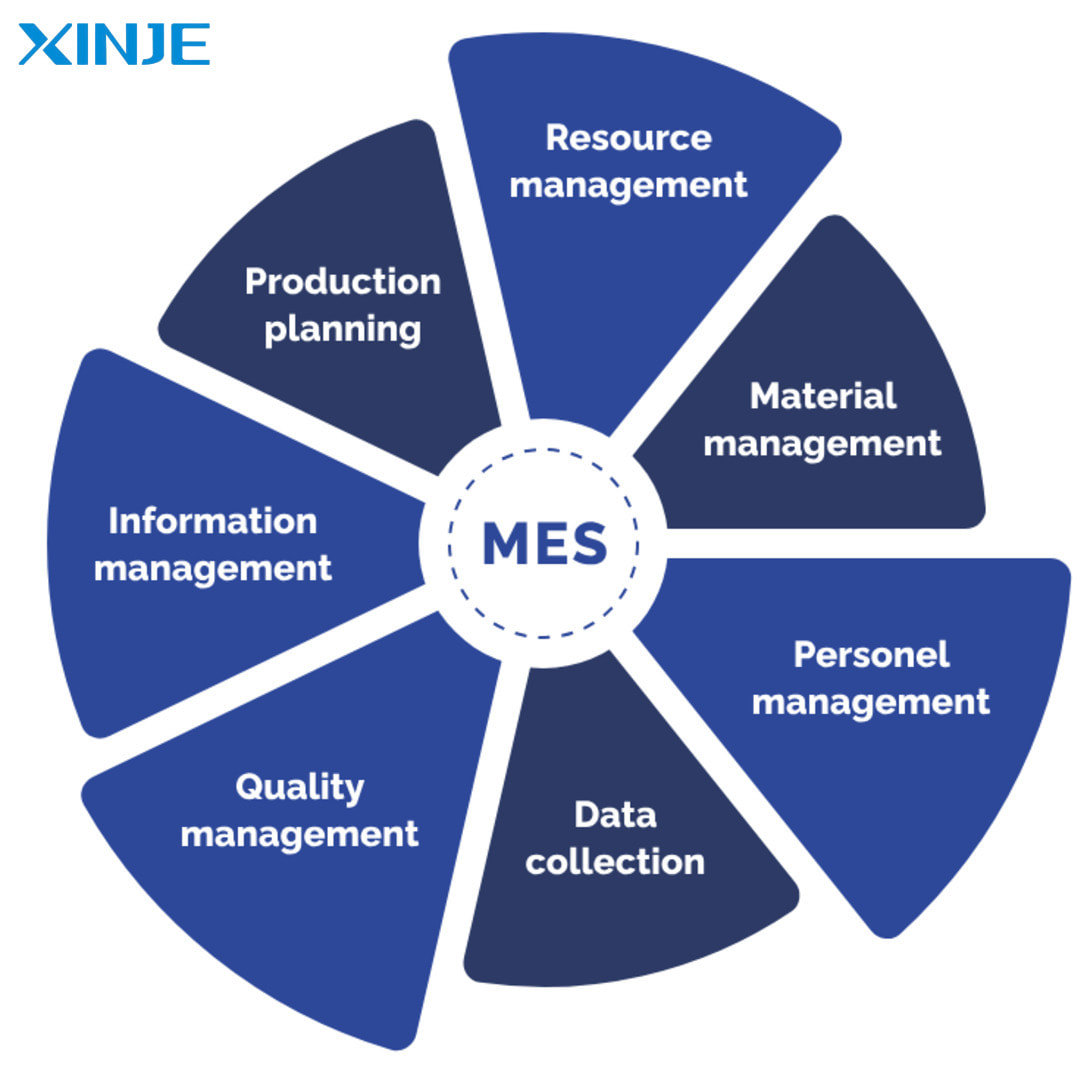
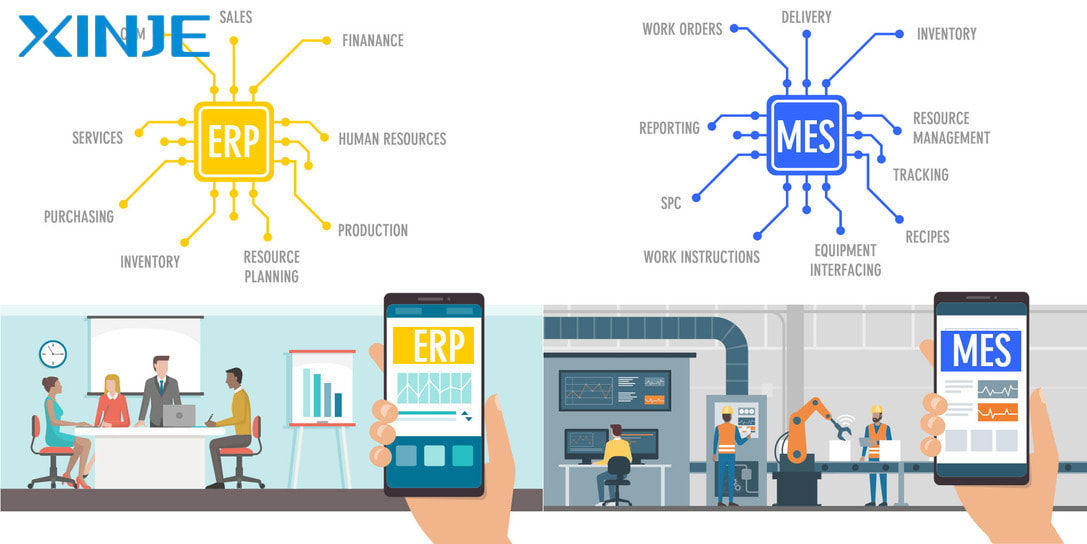
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a software system used to monitor and manage manufacturing operations on the factory floor. MES plays an important role in connecting high-level management systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) with manufacturing equipment on the factory floor. This system provides real-time information about the production process, thereby helping to optimize resource use, manage quality and reduce waste in production.

How does the Manufacturing Execution System work?
Step 1: Data Collection
- MES begins by collecting data from various sources in the factory such as ERP systems, product lifecycle management (PLM) systems, or control devices such as PLCs, SCADA.
Step 2: Data Integration
- The collected data will then be processed and integrated into the central part of the manufacturing execution system. Based on data on raw materials, machine performance and personnel, the system will arrange schedules and allocate resources appropriately.
Step 3: Production planning and coordination
- MES converts targets from the ERP system (such as orders) into specific production plans, detailing each stage. The system allows for schedule adjustments, resource reallocation when incidents occur or requirements change. This helps minimize downtime and maximize performance.
Step 4: Quality management and inspection
- During the production process, the MES system monitors production parameters, compares them with predetermined standards to ensure that the product meets quality requirements. The system automatically records inspection data in real time, reducing the risk of human error.
Step 5: Analysis and reporting
- At this stage, the MES system will synthesize the collected data to create detailed reports on the performance, product quality, and productivity of each type of machinery in the factory. This helps businesses make more accurate decisions in optimizing the production process.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Manufacturing Execution System?
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) plays an important role in optimizing production processes and improving competitiveness. However, like any advanced system, MES not only brings many significant advantages but also comes with challenges that require investment and close management. Below are the outstanding benefits as well as the disadvantages that businesses need to consider when implementing MES systems.
Advantages
- Improve production efficiency: MES helps optimize production processes by providing real-time data on machine status, human resources, and progress. Thanks to that, businesses can respond quickly to incidents or changes, minimize waiting time and improve productivity.
- Control product quality: MES monitors product quality at each stage, collects data for analysis and detects errors early. This system allows businesses to take immediate improvement measures, reduce product defects and ensure that quality standards are met.
- Reduce inventory: MES provides accurate information on production progress and raw material requirements, helping businesses optimize inventory management. With the ability to flexibly adjust production, MES minimizes excess or shortage of inventory, while reducing storage costs and increasing supply chain efficiency.
- High accuracy: MES systems eliminate the need for manual data entry thanks to automatic data integration between production equipment and management software. This not only reduces errors but also increases accuracy in operating processes.

Disadvantages
- High initial cost: MES implementation requires large costs, including investment in software, hardware and personnel training. In particular, small and medium-sized enterprises often have difficulty balancing costs to apply this system. In addition, future maintenance and upgrade costs need to be taken into account.
- Cybersecurity: MES requires constant data connectivity and integration with other systems in the enterprise, which increases the risk of cyber attacks. Without appropriate security measures, enterprises are at risk of production data leakage or operational disruption.

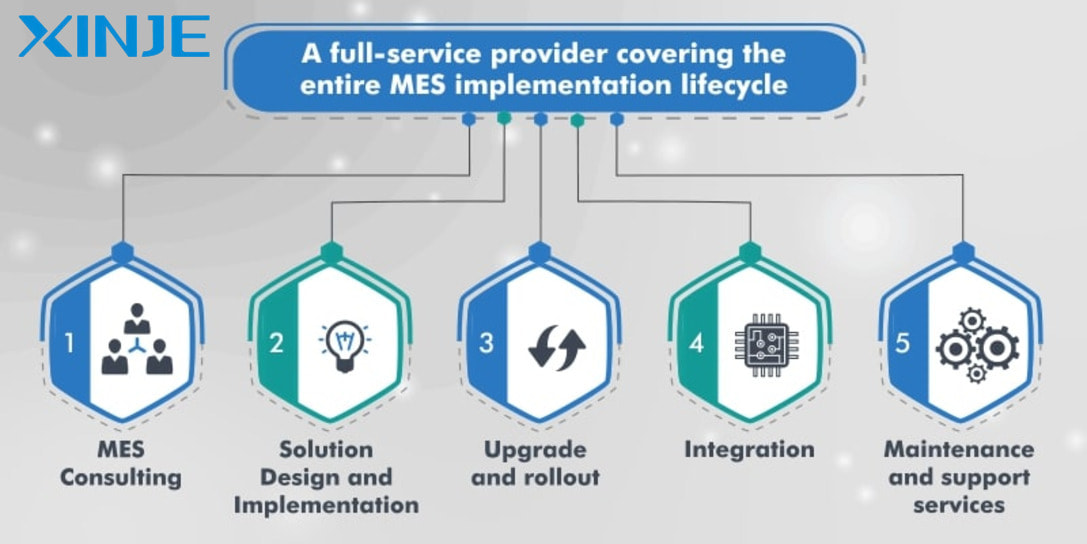
Should MES and ERP be integrated?
Integrating MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is an important step in building a smart factory, ensuring synchronization between senior management and production operations. Here are the advantages of integrating these two systems in the production process.
- Improved decision-making capabilities: Thanks to MES providing real-time data and ERP analyzing to support management strategies. This ensures that decisions are made based on real-time data instead of guesswork.
- Improved operational efficiency: By automating and accurate production planning execution, and updating inventory and distribution information in a timely manner.
- Improved synchronization: Synchronizing data between MES and ERP eliminates information fragmentation, ensuring continuous information flow
- Cost savings: Integration helps reduce manual errors when entering data between the two systems. The time required to process relevant information is also reduced, thereby optimizing operating costs.
A practical example illustrating the benefits of MES and ERP integration can be seen in an automotive parts manufacturing plant. When a new order is processed by ERP, MES automatically generates a production plan based on the order data. MES then monitors progress and updates product status, helping ERP track inventory and notify customers. This process not only reduces processing time but also optimizes operational efficiency.
In short, MES and ERP integration is essential for modernizing manufacturing businesses. For large enterprises, integration is a must to increase competitiveness and scalability. For small and medium-sized enterprises, it is possible to start with simple modules to optimize costs and efficiency.

Conclusion
The Manufacturing Execution System plays a key role in optimizing and modernizing production processes in the automation industry. With the functions of resource management and production monitoring, MES helps businesses reduce costs, improve quality and maximize production efficiency. However, the implementation of this system also faces some challenges in terms of cost and system integration. However, with the development trend of Industry 4.0, MES will certainly continue to be an important tool to help factories improve production processes and achieve higher competitiveness in the market.






