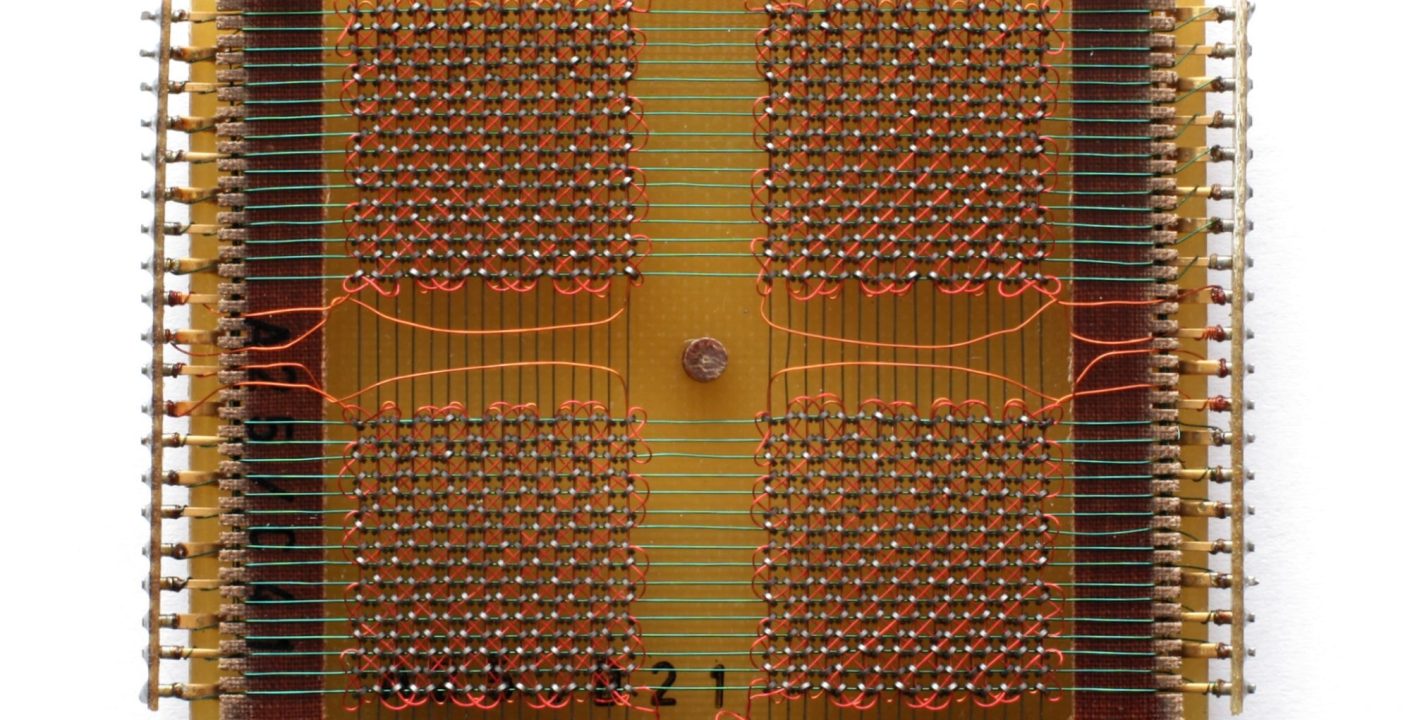
Magnetic core memory, commonly known as core memory, is an early form of random access memory (RAM) that was widely used in computers from the 1950s to the 1970s. It consists of small magnetic rings, called cores, that store information by their magnetization direction. Each core represents a single bit of data and can be magnetized in either direction, corresponding to a binary 0 or 1.
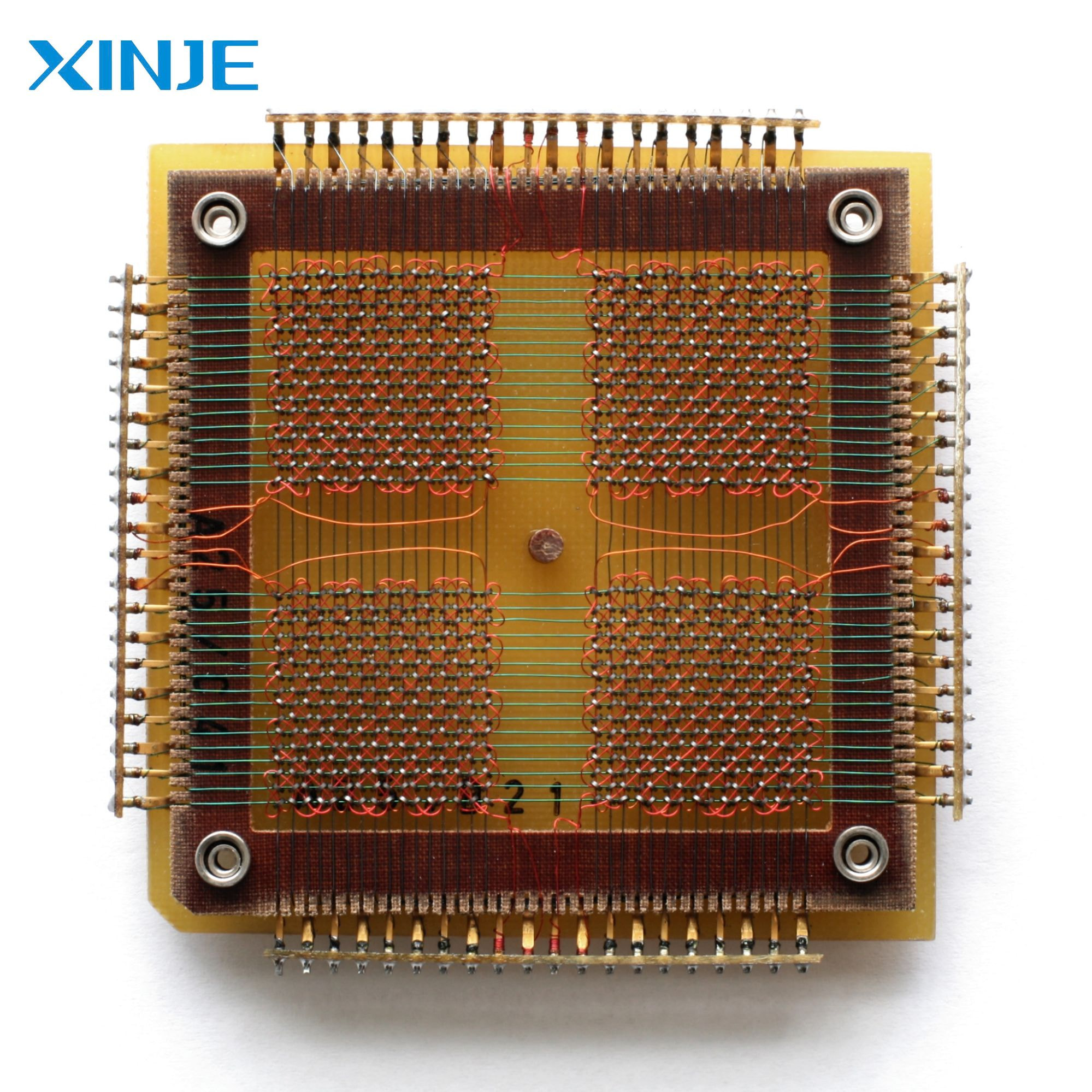

Core memory played an important role in the development of computer systems. It provided optimal storage capacity, especially since it retained data even when the power was turned off. This technology was eventually replaced by semiconductor memory but remains an important milestone in the history of computing.
What are the features of the magnetic core memory?
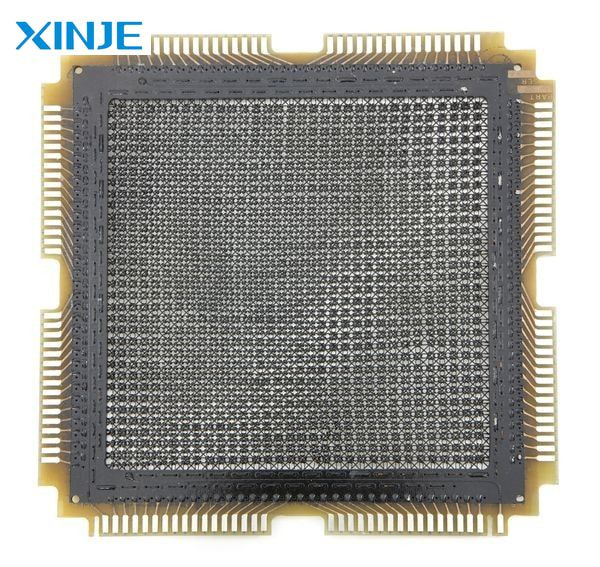

Magnetic core memory is famous for its several unique features that made it a revolutionary technology for digital data storage:
- Non-volatile storage: Unlike modern DRAM, which loses data when powered off, core memory stores data indefinitely.
- Durability and reliability: Magnetic cores are highly resistant to radiation and electrical interference, making them ideal for military and aerospace applications.
- Random access: Unlike sequential memory systems, core memory allows direct access to any stored bit, improving computational efficiency.
- High speed: Core memory provided much faster access than previous storage methods such as delay lines or drum memory.
- Hand assembly: Due to the extremely small size of the cores and the complexity of wiring them together, core memory was labor-intensive to manufacture.
What are the components of magnetic core memory?
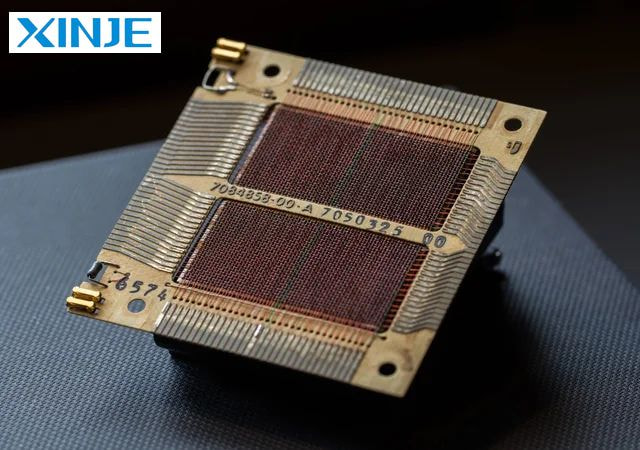

The core of a magnetic core memory system is quite simple in structure, consisting of components such as wire arrays, frame or grid structure, and the entire core control circuit.
- Wire array: The main function of this part is to support the magnetic core to support the control of the wire array to store and retrieve data. These wires usually include: X and Y wires, sensor wires, and inhibitor wires.
- Frame or grid structure: This part will ensure organized and efficient data access because typically, the grids are designed in a configuration such as 64×64 cores per plane. This layout not only simplifies memory organization but also allows multiple bits to be accessed in a controlled manner.
- Control circuit: The entire core memory system relies on the control circuit, which ensures that the appropriate current levels are applied to the X and Y control wires, sensor wires, and inhibitor wires.
How does magnetic core memory work?
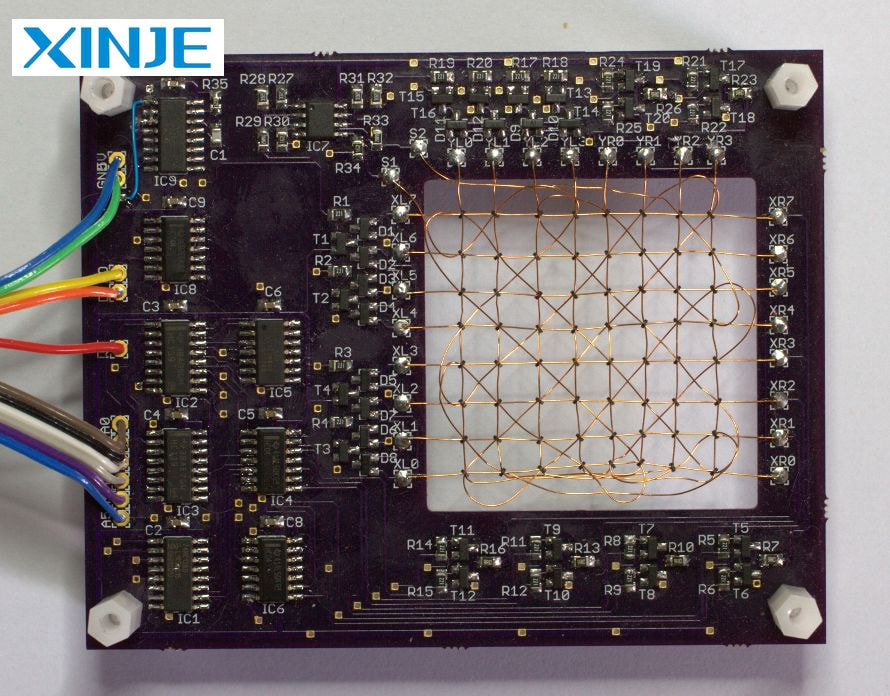

Magnetic core memory operates on the principle of hysteresis, in which each ferrite core can be magnetized in either direction, representing binary values of 0 and 1, and this operation is carried out through three basic steps: data writing, data reading, and memory organization.
- Data writing: To store a bit of data, a specific core in the magnetic memory is selected by sending a current pulse through the X and Y wires. If a positive pulse is applied, the magnetization of the core will flip in one direction and a negative pulse will flip in the opposite direction.
- Data reading: The reading process is destructive because reading the state of the core will change the magnetization of the core. A read pulse is sent through the X and Y wires. If the core is in a certain magnetic state, it will flip and create a voltage in the sensor wire, which the system will detect and determine the stored bit.
- Memory organization: After the above two steps are completed, the cores are arranged in a matrix format, usually 64×64 bit planes or similar structures. If more planes can be stacked and store more data.
Where are magnetic cores memory commonly used?
Although it has been replaced by magnetic core memory today, it was once widely used in computers and specialized systems such as:
- Early mainframe computers: The IBM 1401, IBM 360, and UNIVAC relied heavily on core memory, providing reliable and relatively fast memory for storing and processing data.
- Aerospace and military applications: Magnetic core memory is used in guidance systems for spacecraft, missiles, and aircraft due to its resistance to radiation and harsh environments. It was especially used in the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) that helped navigate the Apollo missions to the moon.
- Industrial control systems: Magnetic core memory is also used in industrial control and automation systems that require stable, non-volatile memory.
Conclusion
With these outstanding characteristics, it is easy to see that magnetic core memory is a breakthrough technology that plays an important role in the development of computer storage. Its durability, non-volatility, and reliability made it the preferred memory system for early computers, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Although it was eventually replaced by semiconductor-based memory, its impact on the history of computing is still significant. Core memory paved the way for modern RAM and influenced the development of memory storage technologies used today.






