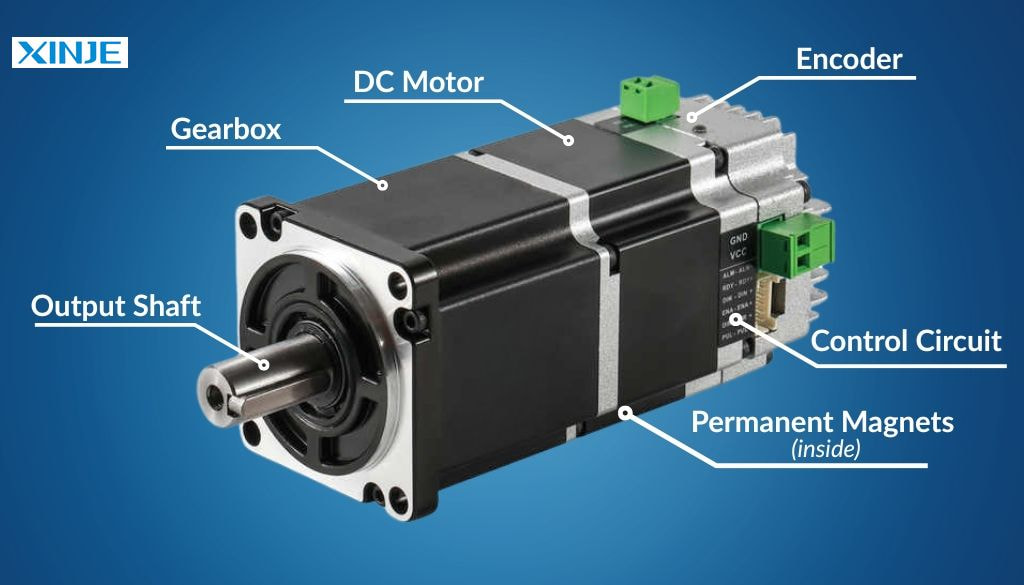
What is the DC servo motor? A DC servo motor is a type of rotary actuator that allows precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration using a DC power supply. It combines a traditional DC motor with feedback devices, such as encoders or potentiometers, and a controller, enabling it to achieve highly accurate movement.
Unlike regular DC motors, a DC servo motor is part of a closed-loop system, meaning the motor’s output is constantly monitored and adjusted to match the desired input signal.
Where are DC servo motors used?
DC servo motors are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, CNC machinery, medical equipment, and aerospace systems, wherever precise motion control is required. Here are some specific applications:
- CNC machines: For precise tool positioning and cutting path control.
- Robots: In robot arms for precise joint movements.
- Textile machines: For maintaining tension and controlling motion.
- Packaging systems: For synchronizing conveyors and labeling heads.
- Medical devices: In surgical robots and infusion pumps that require smooth, responsive motion.
- Antenna positioning systems: Where precise angular motion is required.
- Camera gimbals: For stabilization and smooth pan/tilt motion.
Their affordable price and simple implementation make DC servo motors the ideal solution for low- to medium-torque applications that require high sensitivity.
What is the working principle of a DC motor?
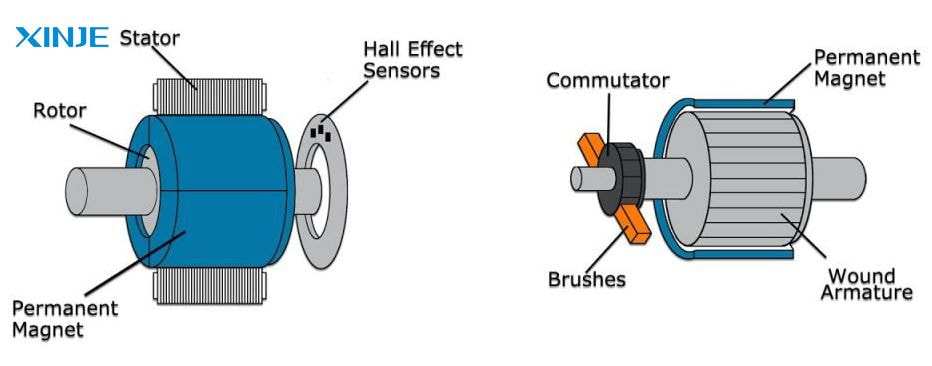

DC servo motors operate on the principle of electromagnetism, but have a different feedback mechanism than a regular DC motor through the following steps:
- Input signal: A control signal (usually from a microcontroller or PLC) determines the desired position or speed.
- Motor activation: The DC motor receives voltage and starts rotating.
- Feedback device: An encoder or potentiometer measures the actual position or speed of the motor.
- Error correction: The feedback signal is compared to the input signal by the controller (PID loop). If there is a mismatch, the controller adjusts the voltage or direction to minimize the error.
- Closed-loop control: This continuous monitoring and adjustment form a closed loop, ensuring that the motor output exactly matches the desired command.
This mechanism enables precise control of position, speed, and torque, even under varying load conditions.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of DC servo motors?
Advantages of a DC servo motor
DC servo motors have outstanding advantages in the automation industry. Some of the outstanding advantages of DC motors include:
- Accurate control: The built-in feedback system allows for highly accurate positioning, which is important in robotics and CNC systems.
- Fast response time: DC servo motors can accelerate and decelerate quickly, making them ideal for operations that require rapid changes in direction or speed.
- Simple control mechanism: Compared to similar AC servo motors, the control circuit of DC servo motors is generally simpler, making integration easier.
- Compact and lightweight: DC servo motors are typically smaller and lighter, which is beneficial for applications with limited space.
- Cost savings: For many automation systems, especially small-scale systems, DC servo motors offer a better price/performance ratio.
Disadvantages of a DC servo motor
Although DC servo motors have many outstanding features, there are still some limitations that operators need to pay attention to, such as:
- Maintenance requirements: Most DC servo motors have carbon brushes and commutators, which wear out over time and require periodic maintenance.
- Limited service life: Due to mechanical wear, the operating life is shorter than that of brushless servo motors or AC servo motors.
- Lower power handling: DC servo motors are generally not suitable for high power or high torque applications, while AC servo motors perform better.
- Heat build-up: Operating at high speeds or changing loads frequently can lead to increased heat build-up, affecting performance.
- Vulnerable to electrical interference: In sensitive environments, the commutation process can generate noise that interferes with other electronic devices.
What is the difference between AC and DC servo motors?

Choosing between AC and DC servo motors depends largely on your application’s requirements for power, precision, cost, and control complexity. While both types serve the same fundamental purpose, accurate motion control, they differ significantly in terms of performance characteristics, maintenance needs, and suitable use cases. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision.
| Feature | DC servo motor | AC servo motor |
| Control Complexity | Simpler control | More complex control |
| Torque and Power Output | Suitable for low to medium torque | Better for high torque and industrial-grade power |
| Speed Control | Excellent at low speeds | Better for high-speed |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically more expensive |
| Application | Light-duty systems | Heavy-duty automation, industrial robotics |
Conclusion
DC servo motors remain a cornerstone of precision automation, offering a versatile, cost-effective solution for a wide range of motion control applications. Their closed-loop design, fast response, and accurate control make them an excellent choice for industries like manufacturing, robotics, and medical devices.
However, it’s essential to weigh their advantages against their limitations, particularly regarding maintenance and power handling, before selecting a motor for your system.