In industrial servo systems, choosing the right output signal standard such as PNP (sourcing output) is a key factor to ensure stable connection between sensors, drivers and PLCs. PNP operates on the principle of “positive power output”, which is easily compatible with many modern control devices. XINJE’s article will help you understand what PNP signal is, what its advantages are and when to choose PNP instead of NPN in servo systems.
What is Sourcing Output (PNP)?
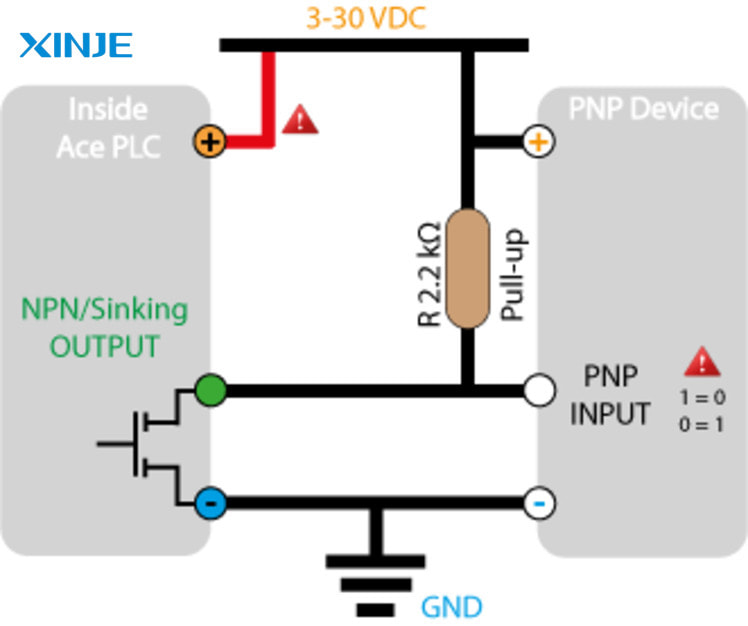
In the field of automation, Sourcing Output (PNP) is a type of electrical signal output in which the signal output device (such as PLC, servo driver, sensor) supplies positive voltage (+V) to the load when in ON state. At that time, the other end of the load will be connected to ground (GND) to complete the electrical circuit.
In other words, PNP output “sourcing” current, meaning pushing current from the positive source through the load to GND.
What are the advantages of Sourcing Output (PNP)?
In industrial control systems, especially automated servo systems, PNP output is increasingly preferred due to the following advantages:
- Safer to touch: With PNP, the output signal is a positive source, so when there is a contact problem or wrong connection, the possibility of causing shock or short circuit is lower than with NPN output (ground). This is the reason why systems in Europe often prefer PNP.
- Less noise in industrial environments: Due to the high voltage signal transmission (+24V), the PNP signal is more stable and less affected by noise from surrounding machinery, especially in long wires connecting the driver and PLC.
- Good compatibility with digital inputs of many modern PLCs: Most PLCs such as Siemens, Mitsubishi, Omron, etc. support PNP input well, making the connection and programming process simple, minimizing technical errors.
- Easy to diagnose logic status: Because a high logic signal level (+V) corresponds to the ON state, monitoring and checking the device status via indicator lights, meters or monitoring software is easier to understand.
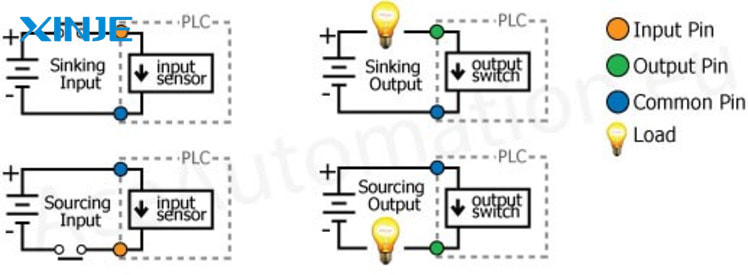

When to choose PNP for servo systems?
Choosing PNP (sourcing output) or NPN (sinking output) output not only depends on technical preferences, but is also directly related to system compatibility and operational safety. Here are some criteria to help you determine which PNP to choose:
- Use a PLC that supports PNP input: If the main controller (such as a PLC or HMI) requires a high logic level (+24V) to activate the signal, PNP is the right choice.
- Input sensors and relays also use PNP: The system will be more stable if all devices have the same signal type. Avoiding mixing PNP and NPN will help simplify the circuit diagram and limit logic errors.
- Safety and low noise requirements: In industrial environments with a lot of electrical noise or requiring better operator protection, PNP outputs are often preferred.
- In case of upgrading an old system: If the system is using NPN but you want to upgrade to a new device (servo driver, PLC, etc.) that better supports PNP, consider synchronizing the entire signal.
What are the notes when designing or connecting PNP signals?
To ensure the PNP signal operates stably and safely in the servo system, it is necessary to remember some of the following technical principles:
- Connect the power source and PLC logic in the correct direction: The PNP output is +V, so the PLC input or receiving device must be connected to GND. Incorrect connection can cause the input to burn or not receive the signal.
- Check the output load: Clearly determine the maximum current that the PNP output can withstand to avoid overloading when controlling relays, contactors or power devices.
- Anti-interference and circuit protection: For industrial applications, it is recommended to use anti-reverse diodes, filter capacitors or isolation optocouplers to protect the output from voltage spikes or interference from high-power devices (such as servo motors, inverters, etc.).
- Separate signal wires and power wires: Helps reduce cross-talk, ensuring stable PNP signals in automation systems with many devices operating at the same time.

Common errors when using PNP and how to fix them?
Although PNP signals are considered safe and popular in control systems, if users do not understand the operating principles and connection diagrams, they can still easily encounter the following errors:
Incorrect input voltage supply
- Cause: One of the common errors is the incorrect voltage supply from the PNP output to the receiving device such as PLC, servo driver or sensor. This can happen when the system uses multiple sources or devices from different manufacturers.
- How to fix: Check the allowable voltage range (usually 24VDC); make sure the source and device use the same standard.
Incorrect signal polarity
- Cause: With PNP signals, the “sourcing” output supplies positive power, while the load is connected to GND. If the polarity is incorrect (for example, connecting the load to V+ instead of GND), the device will not operate, or worse, it can cause a short circuit or fire.
- Solution: Clearly identify the power (+), signal, and GND pins before connecting; use a voltage meter if necessary.
Unstable signal when the load is small
- Cause: Some input devices (such as microcontrollers, digital input modules) have high impedance, causing the load current through the PNP output to be insufficient to pull the signal stably.
- Solution: Add resistors (10–20kΩ) from the signal to GND; or use buffer circuits, opto-isolation.
Signal noise in industrial environments
- Cause: In factories, electrical signals are often affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI) from motors, inverters, power relays, etc. This especially affects PNP control signals that are long or transmitted over long wires.
- Solution: Attach a flyback diode, filter the signal with a capacitor or opto-isolator.


Conclusion
Sourcing Output (PNP) is a popular output standard in industrial control systems, especially suitable for modern servo control devices and PLCs.
Thanks to its stable positive power supply, easy compatibility and safety in industrial environments, PNP signals are often preferred when designing new control systems.
However, to ensure efficient and safe system operation, users need to understand the operating principles, know how to choose the right device, and pay attention to factors such as polarity, load current, and signal isolation.
Choosing the right signal standard from the beginning will help optimize servo system performance and minimize problems during operation.