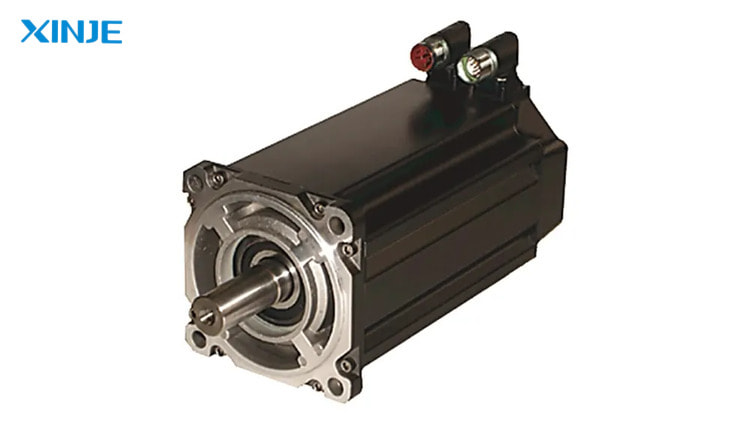
In modern industrial automation systems, AC servo motor plays the role of “moving brain” – precisely controlling position, speed and torque in real time. Thanks to its fast response, stable operation and easy integration with PLC/HMI, this type of motor is widely used in production lines, industrial robots, CNC machines… So what is AC servo motor? Let’s find out with XINJE in the following article.
What is an AC Servo Motor?
AC servo motor is a type of AC electric motor specially designed for use in motion control systems that require high precision and fast response. This type of motor is often combined with a driver and an encoder to form a closed servo system.
Linkage between motor – encoder – driver
- These three components form a closed-loop control system:
- The controller (controller or PLC) sends command signals (position, speed, torque to be achieved) to the driver.
- The driver supplies appropriate power to the motor, causing the rotor to rotate.
- As the rotor rotates, the encoder records the actual position and speed, sending feedback signals to the driver.
- The driver compares the feedback signal with the control signal. If there is a deviation, the driver automatically adjusts the voltage/frequency to correct the motion.
This process occurs continuously in real time, ensuring that the motor always runs correctly as required.
How many parts does an AC Servo Motor consist of?
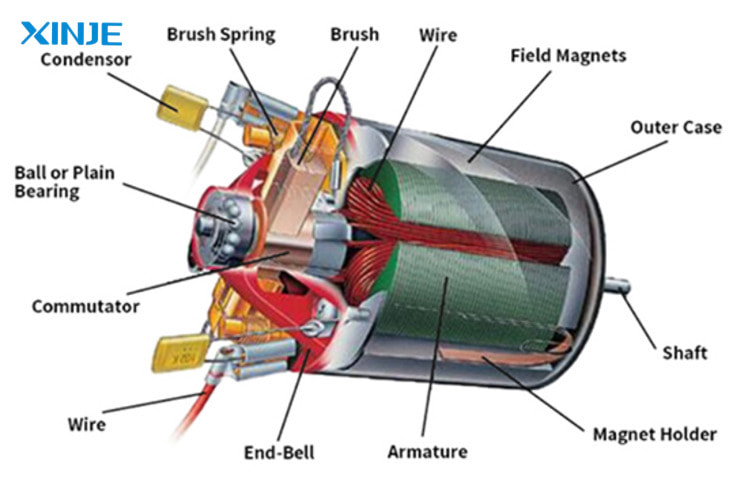
An AC servo motor is not just a simple electric motor, but a system that closely coordinates mechanical – electrical – control components, ensuring high precision in each movement. A basic AC servo motor usually includes the following 4 parts:
- Stator: Is the static part, creating a magnetic field when supplied with AC power. This magnetic field will act on the rotor to create movement.
- Rotor: Is the rotating part, usually attached directly to the load shaft or actuator. The rotor rotates under the control of a variable magnetic field.
- Encoder (feedback sensor): Attached to the rotor shaft to collect information about position, speed and direction of rotation. The encoder sends this signal to the driver to maintain control accuracy.
- Driver (power controller): Is the intermediary part between the main controller (PLC, controller) and the motor. The driver decodes the control signal and supplies the appropriate voltage to the motor, while receiving feedback signals from the encoder for continuous calibration.

What are the advantages of using AC Servo Motor in the factory?
AC servo motor not only meets strict technical requirements, but also brings many practical benefits to automation lines. Here are the reasons why this type of motor is increasingly popular in manufacturing plants:
- Absolute precision: AC servo motor has the ability to control position and speed with extremely small deviations, ensuring that the output product always meets the standards. The closed-loop control mechanism helps the motor respond quickly and operate smoothly even when the load changes.
- Flexible application in many types of machinery: With many different power and torque ranges, AC servo motors are suitable for a range of equipment such as: Automatic packaging machines, 6-axis industrial robots, CNC machines, labeling machines, sorting machines, etc.
- Easy to connect and integrate the system: Modern AC servo motors often come with drivers that can flexibly connect to central control devices such as PLC, HMI or SCADA, supporting communication via popular industrial standards: Modbus, EtherCAT, CANopen…
- Energy saving: Because the motor only operates exactly as required (not running continuously), it saves significant energy compared to conventional motors.
- Fast response: Extremely fast response time thanks to closed-loop control mechanism and high-resolution encoder. Ensure precise movement as soon as the control command is received, limiting error-causing delays in high-speed production lines.


What is the difference between AC Servo Motor and DC Servo Motor?
Although both are types of motors used in servo systems, AC servo motors and DC servo motors have many distinct differences in structure, performance and application capabilities:
| Criteria | AC Servo Motor | DC Servo Motor |
| Power supply | Alternating current (AC) | Direct current (DC) |
| Structure | No carbon brushes – smooth operation, less wear | With carbon brushes and commutators – easy to wear, requires periodic maintenance |
| Lifetime | Higher, less maintenance required | Lower, prone to carbon dust generation |
| Efficiency & stability | High, stable operation even when the load changes | Lower efficiency, prone to slippage when the load increases suddenly |
| Response speed | Very fast – suitable for complex movements | Very fast – suitable for complex movements |
| Applications | Industrial robots, CNC machines, high-speed automation lines | Industrial robots, CNC machines, high-speed automation lines |
| Initial cost | Initial cost | Lower |
| Control accuracy | Excellent – smooth, repeatable position, speed, torque control | Relatively – less suitable for high precision requirements |
| Integration with industrial systems | Easy to integrate with PLC, HMI, SCADA via industrial communication protocols | Limited, mainly standalone or simple control |

What are the criteria for choosing the right AC Servo Motor for your factory?
Choosing the right type of AC servo motor not only ensures optimal operating performance, but also helps minimize failures, save costs and extend system life. Here are the important criteria that businesses need to consider before investing:
- Based on technical parameters: power, torque and speed: Choose a motor with enough power and torque to operate the load without overloading or wasting. The motor speed also needs to match the operating cycle of the machine.
- Compatibility with driver and control system: The motor must be compatible with the existing driver in terms of voltage, signal standards and communication protocols such as Modbus, CANopen or EtherCAT. Avoid choosing a motor that requires the system to change the entire control configuration.
- Meeting installation environment conditions: Factors such as temperature, dust, humidity, vibration, etc. need to be considered to choose a motor with the appropriate IP protection level. Otherwise, the motor will quickly break down and affect the entire line.
- Brand and long-term stability: Prioritize reputable brands like XINJE to ensure quality, easy maintenance and technical support. Industrial motors should be invested in the long term instead of choosing a cheap price at first.
Conclusion
AC servo motor is not only a simple actuator but also a core component in modern control systems, helping to improve accuracy, increase speed and optimize performance for the production line.
With fast response, precise control and flexible integration, this type of motor is becoming the standard choice in many industries from packaging, food to robot automation.
If your business is looking for a high-quality motor solution that is easy to integrate and operates stably for a long time, AC servo motor is a worthy investment.
Contact XINJE now for advice on choosing the motor line that best suits your current system.






