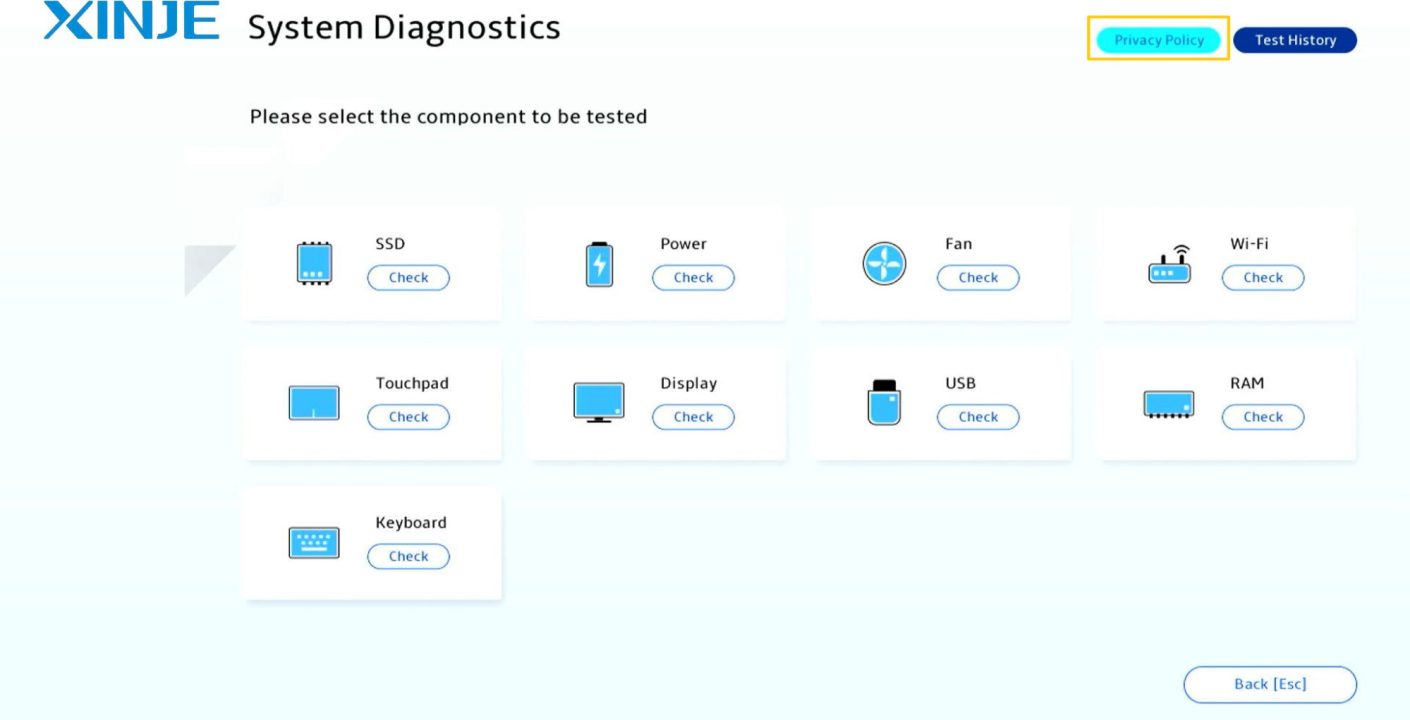
What is the System diagnostics? In today’s industrial automation landscape, system diagnostics refers to the process of monitoring, analyzing, and troubleshooting the health and performance of equipment, software, and network infrastructure. These diagnostics help ensure that automated systems operate reliably, efficiently, and safely by identifying issues before they lead to downtime or failure.
Whether you are monitoring a production line, managing PLC, HMI integration, or maintaining a SCADA system, system diagnostics play a vital role in keeping your operations online and optimized.
How can I perform system diagnostics?
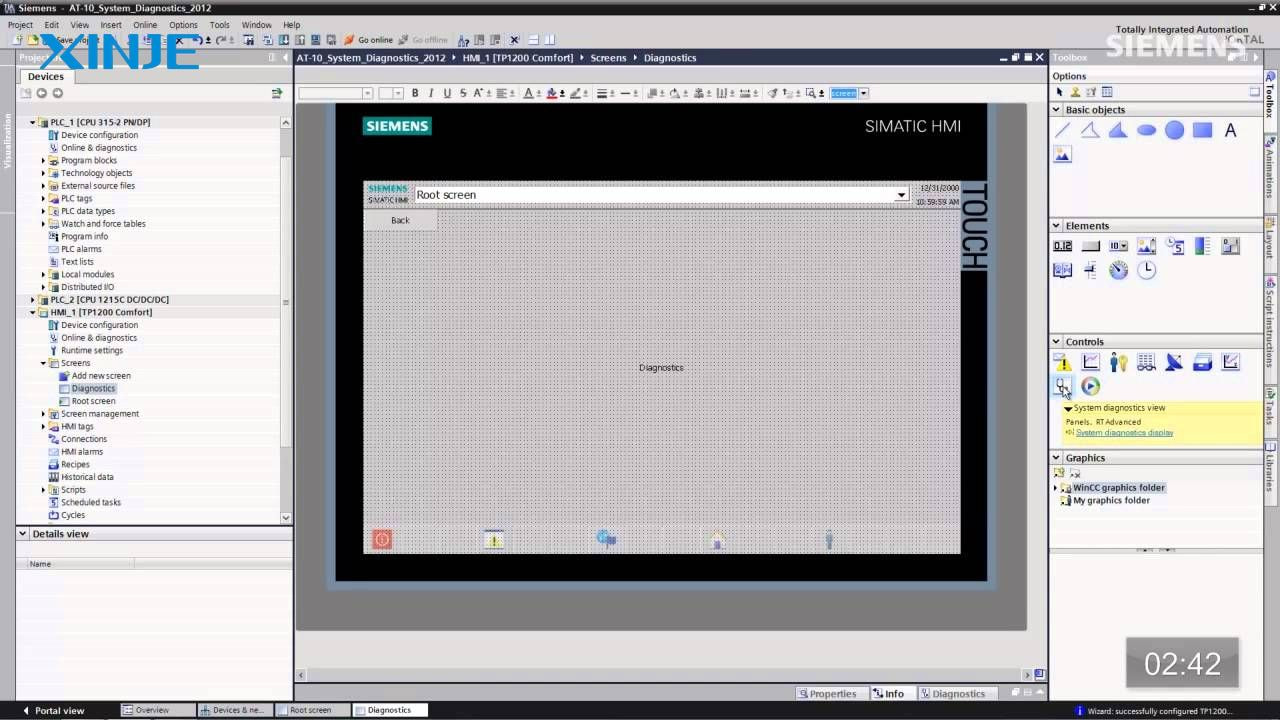

Performing system diagnostics in an industrial environment involves a variety of processes, tools, and best practices to assess the health of your automation system. The exact steps may vary depending on the type of HMI, PLC, and industrial network used, but here are the core components:
- Utilize built-in diagnostic tools, such as alarm logs, system logs, communication status indicators, or tag monitors, to verify network or HMI connectivity in real-time.
- Monitor CPU and memory usage: If your HMI runs on a PC-based system or embedded operating system, it is necessary to check hardware health, such as CPU temperature and usage, disk I/O performance, and application crash logs, to be able to see memory leaks and diagnose them in time
- Network diagnostics: In Ethernet-based industrial networks (e.g, Modbus TCP, PROFINET, Ethernet/IP), communication reliability is essential to detect packet loss, monitor latency between devices, or identify misconfigured IP addresses or subnet conflicts
- Perform manual and automated checks: Combining automated health checks with manual checks will provide a more accurate picture, such as daily tag scanning or integrity checks, cable checks, temperature, dust buildup, or mechanical damage.
What is the purpose of System Diagnostics?
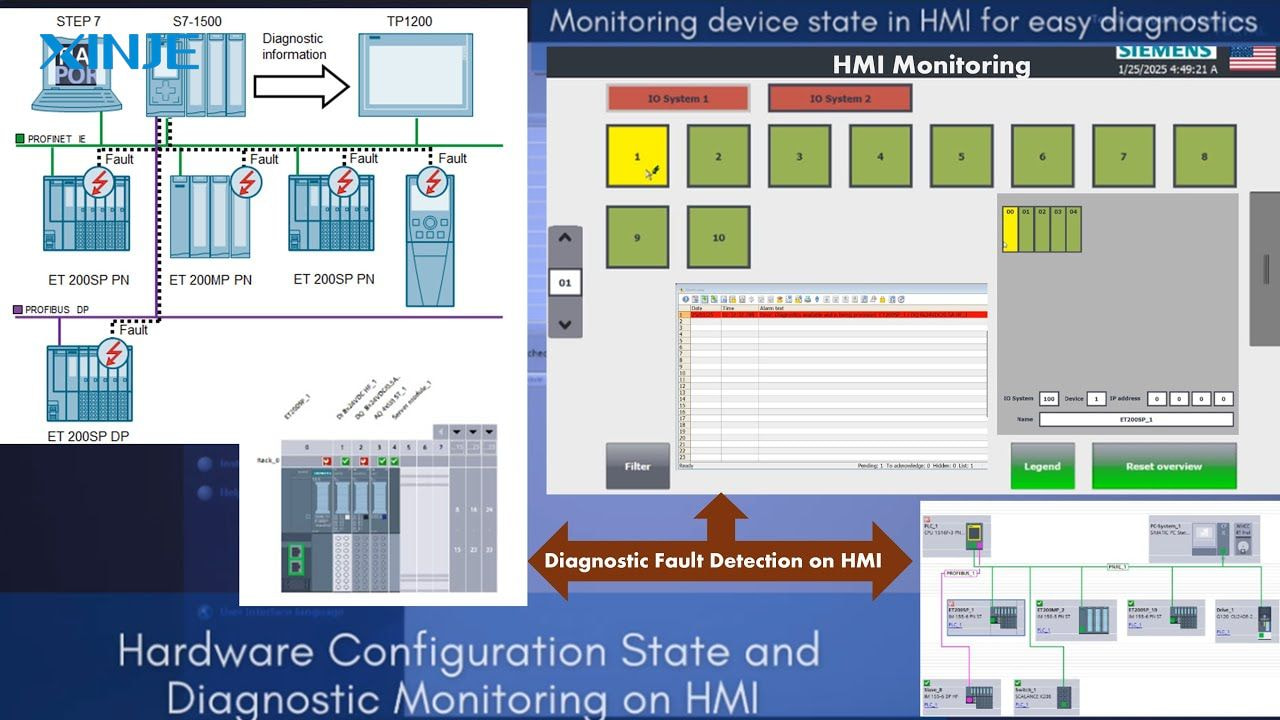

System diagnostics is not only a troubleshooting tool but also a proactive strategy. With many beneficial purposes for the system as follows:
- Preventing equipment downtime by early identification of component degradation, flagging network interruptions, and triggering preventive maintenance alarms. This can detect a failed motor driver before it stops the conveyor system if current abnormalities are recorded and diagnosed early.
- Improving operational safety, ensuring safety relays and sensors operate as expected, the emergency stop circuit (E-Stop) is continuously monitored to ensure system consistency.
- Support predictive maintenance strategies: data collected through system diagnostics can be used to create machine learning models for predictive maintenance, such as temperature drift trends over time, motor vibration frequency data, or cycle count analysis…
- Ensure compliance and reporting: Many industries require rigorous recording of operational data. Diagnostics can record fault resolution times, operator access history, and logs.
What does the system diagnostic process do?
The system diagnostic process is a multi-layered process that continuously monitors, checks, records, and alerts users to the operating status of automation systems. Let’s analyze each step:
- Step 1: System initialization check, when starting or rebooting, the connected HMI and PLC will self-check to verify the software license, detect I/O modules, and scan firmware compatibility.
- Step 2: Runtime monitoring, after running, the system diagnostic process continuously checks the heartbeat signal of the device, the PLC-HMI card communication status, the response time of the sensor, and the response delay of the HMI screen
- Step 3: Event and alarm logging, when an error or abnormality is detected, the log will be saved, or notifications will be sent via email, SMS, or local alarm. The operator may then be asked to confirm the error before continuing.
- Step 4: Remote diagnostics, advanced HMIs enable remote diagnostics via Ethernet or cloud integration. Operators can access system logs remotely, perform real-time monitoring from a centralized dashboard
- Step 5: User interface feedback, a good system diagnostic process will integrate feedback into the HMI interface, color-coded status indicators (green/yellow/red) combined with visual charts, operators can make informed decisions without having to search through multiple menus or software platforms.
Conclusion
In short, system maintenance and diagnosis are essential tasks that operators need to perform to maintain the performance of HMI and PLC to ensure the safety of everyone in the factory, and also help the system always operate flexibly and intelligently.
By continuously monitoring hardware, communication, and process data, these tools help detect problems early, streamline troubleshooting, and minimize costly downtime. Whether you’re upgrading your HMI or expanding your SCADA system, make diagnostics a key part of your automation roadmap.