In automation systems, Communication Timeout is a common communication error that can cause the HMI to lose connection with the PLC or other control devices. If not detected and handled promptly, this error will cause interruptions in the production line, data loss and costly maintenance. The following article will help you understand what Communication Timeout is, its causes, effects and the most effective solutions.
What is Communication Timeout?
In the field of automation, Communication Timeout is understood as a state of disconnection or interruption of communication between control devices — typically between HMI (Human Machine Interface) and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), SCADA, or other peripheral devices.
When a timeout occurs, the HMI will not receive response data within the specified time period, thereby causing errors or stopping operations.
HMI is an intermediate interface that allows operators to monitor and control machines. When the HMI has a Communication Timeout, the operator cannot update the device status, cannot control the process, or the display parameters are incorrect.
Therefore, Communication Timeout is considered a typical communication error that any automation engineer needs to understand when designing, installing and operating HMI.
When does Communication Timeout occur?
Communication Timeout usually occurs when the HMI cannot receive feedback data from the control device within a certain time period. Some common situations:
- Lost transmission signal: the network cable is loose, broken or the RJ45, RS485 connector is unstable.
- Configuration error: wrong IP address, wrong baudrate parameter, wrong communication protocol selection (protocol) such as Modbus TCP, Profibus, Ethernet/IP…
- Signal conflict: many devices share the same communication bus but do not properly stream, causing data congestion or collision.
- Electromagnetic interference: high-power machines (inverters, motors) emit noise waves, making the transmission signal unstable.
- Device hangs or resets: PLC, SCADA hangs the program or suddenly restarts without HMI having time to synchronize.
These situations often appear unexpectedly, especially with old systems, long-distance network cables or noisy industrial environments. Therefore, the operating engineer needs to regularly check and prepare timely solutions.


What are the main causes of Communication Timeout in HMI?
Hardware error
- Loose network cables & connectors: Physical connections such as Ethernet cables, RS232/RS485 cables, if loose, broken or poorly connected, will cause unstable signal transmission, easily causing timeout.
- Faulty network switch/hub: Intermediate network devices such as industrial switches, signal splitting hubs, if overloaded or with broken ports, will cause communication interruption.
- Faulty communication module: Many HMIs use expansion modules (eg Profibus, Modbus TCP modules) — if the module fails, the signal transmission circuit will become unstable.
Configuration error
- Incorrect IP address or device ID: In Ethernet or RS485 networks, each device needs a unique identification address. If duplicated or incorrect, the HMI will not be able to find the target device.
- Incorrect baudrate and parity parameters: With serial connections, just one incorrect speed or parity parameter can cause data transmission errors.
- Wrong protocol selection: For example, HMI installs Modbus TCP but PLC only supports Modbus RTU, or installs the wrong communication port.
Software error
- Incompatible firmware: HMI or PLC has not been updated to the new version, leading to data conflicts.
- Tag or mapping error: Wrong address data tag, duplicate tag or incorrect mapping order also causes timeout errors.
- Program loading conflicts: When loading/rerunning the HMI project without disconnecting the device, the system may lose synchronization.
Operating environment
- Electromagnetic interference: In the factory environment, inverters and high-power motors emit high-frequency interference waves, which can easily cause signal transmission errors.
- Sudden power loss: Unstable power supply for HMI or PLC, voltage drop, power outage also causes the device to lose connection immediately.
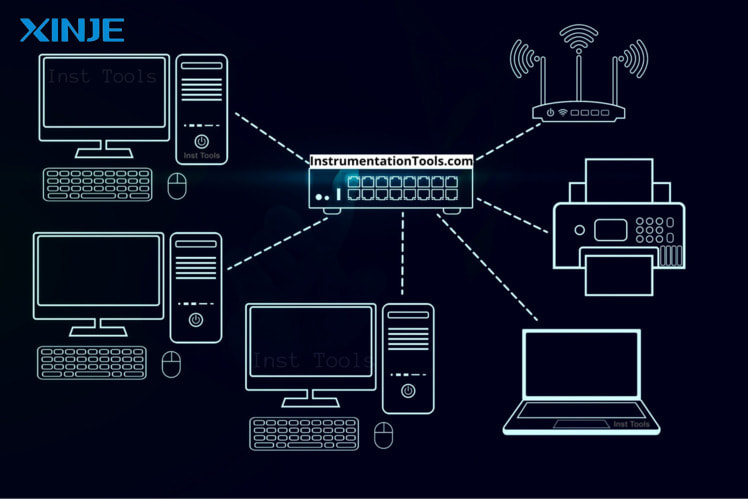

What are the effects of Communication Timeout on automation systems?
Communication Timeout not only causes temporary disconnection but also brings many risks to the automation system. Below are common consequences when HMI has communication errors.
- Stopping the production line: Communication Timeout can cause the HMI to lose the ability to send/receive control commands to the PLC, inverter or robot. At that time, the devices cannot coordinate operations in the correct order.
- Asynchronous data, incorrect reporting: When the connection is lost, data may be missing, incorrect or not recorded, making remote monitoring or management reporting inaccurate. This can easily lead to wrong decisions about production planning, maintenance, and goods receipt.
- Loss of operating & maintenance costs: Frequent Communication Timeout will increase the cost of troubleshooting, replacing components, and calling engineers for repair.
- Impact on productivity & safety: When the HMI is disconnected, the operator cannot monitor the machine status in real time, potentially causing accidents if the faulty equipment or incorrect process is not detected in time.
How to check & handle Communication Timeout?
To limit the damage caused by Communication Timeout, the operating engineer needs to know how to check and handle it promptly. Below are the basic steps to fix the error and maintain a stable connection for the HMI.
- Check the connection status on the HMI: First, observe the error message directly on the HMI screen. Many HMI models clearly display the connection status with the PLC, the device address, or report “No Response”/“Timeout Error”. Identifying the specific error will help narrow down the cause.
- Verify the intermediate cables & devices: Check the entire physical transmission line: Ethernet network cable, RS485/RS232 wire, connectors, switches or hubs. Remove and reinstall the plugs, replace the test cable if there is a suspected hidden break or loose contact.
- Check the IP address, communication port: Compare the IP parameters, subnet mask, communication port and device ID in the settings of the HMI and PLC. Make sure there are no duplicate addresses, wrong ports or wrong protocols (Modbus RTU vs TCP).
- Update HMI firmware & software: Many timeout errors arise due to outdated HMI or PLC firmware, causing conflicts when transmitting data. Download and update the latest software version from the manufacturer, and check the compatibility between the HMI and the control device.


Conclusion
Communication Timeout is a common communication error but can be completely prevented and handled if you understand the cause and how to fix it. Regular inspection, using quality equipment, correct configuration and maintaining a stable operating environment will help the HMI system operate continuously, ensuring a safe and efficient production line.
Enterprises should equip engineers and technicians with basic knowledge to limit risks, save operating costs and improve the reliability of the entire automation system.






