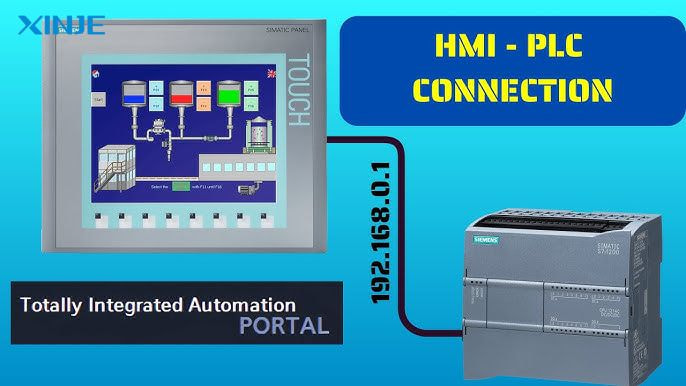
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a dedicated industrial computer designed to control machines, processes, or equipment in real time. A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is a user interface that allows operators to interact with industrial control systems such as PLCs. It can be a touch screen panel, a computer-based SCADA interface, or a keyboard display.
Both HMI and PLC often work together as a complement to each other, which is commonly seen in many automated manufacturing processes. But sometimes, HMI and PLC cannot connect, so what is the reason? Let’s find out in the article below! believe
How do HMI and PLC work together?
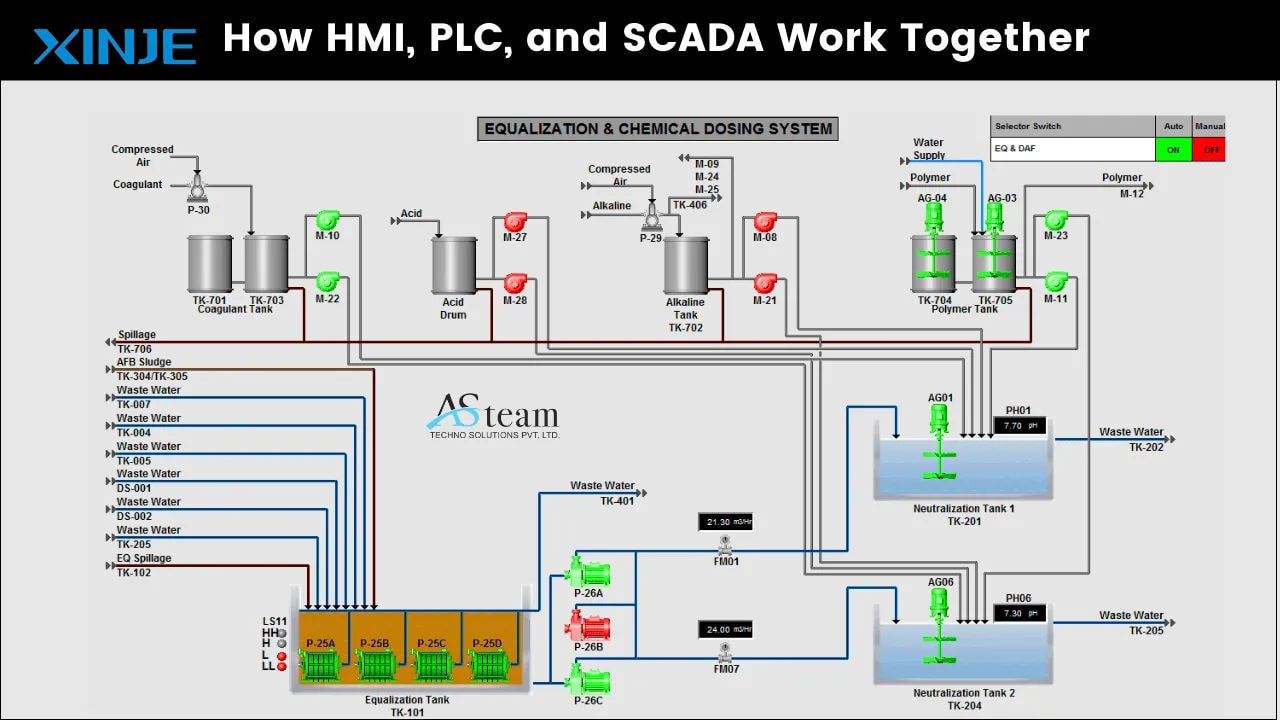

HMI and PLC operate in a client-server model where the PLC acts as the server, providing data to the HMI. The HMI acts as the client, requesting or polling data from the PLC.
This communication process is usually done through common industrial protocols such as:
- Modbus TCP/RTU
- Ethernet/IP
- Profibus
- OPC UA
- Siemens S7 Protocol
The connection between the two devices is established via physical media such as Ethernet, RS-232/RS-485 serial cable, or wireless module. The HMI sends read/write requests to PLC memory addresses, allowing the operator to visualize or control variables in real time.
Therefore, when this connection is lost, the HMI may display “PLC not connected”, “communication timeout,” or similar errors, making it impossible for the operator to view and control manually.
Why does the HMI lose connection with the PLC?

There are several reasons why an HMI may lose connection to a PLC. Determining the cause of the problem is important, as this will be the basis for finding a solution to restore normal operation. Common causes include:
- Network cable or port problems: Loose or damaged Ethernet or serial cables, bent connectors, or faulty switch ports can cause intermittent or complete loss of connection.
- Incorrect IP configuration: If the HMI and PLC are not on the same subnet or the IP addresses are duplicated or misconfigured, communication will fail.
- Protocol mismatch: Using the wrong communication protocol or improper settings (baud rate, parity, number of stations) can result in errors.
- HMI configuration errors: Incorrect tag mapping, driver settings, or outdated project files in the HMI software can cause the software to request invalid data.
- Device Firmware Incompatibility: Outdated firmware on the HMI or PLC can cause issues at the protocol level.
How to reconnect the PLC and HMI?
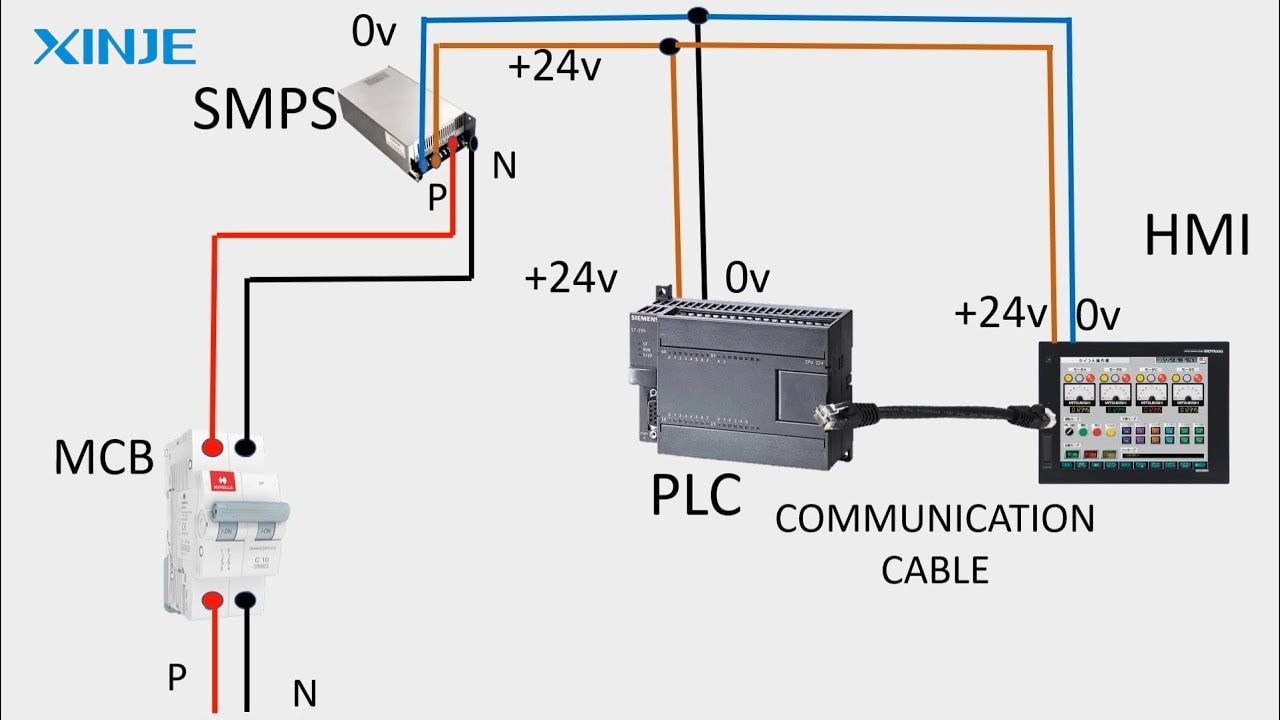

To resolve the connection error, a systematic approach is required. Some basic checks and troubleshooting steps can be referred to:
- Check the physical connection to ensure that the Ethernet or serial cable is securely plugged in. Additionally, check the cable, router, switch, or communication module.
- Confirm the IP address settings to ensure that static IP addresses are assigned correctly. Also, check that there are no IP address conflicts in the network.
- Match the protocol and driver settings: The operator will open the HMI configuration software and double-check the protocol selection (e.g., Modbus TCP vs. Modbus RTU) to verify the correctness between the two devices
- Restarting both devices is also a common way to reset the connection stack.
Those are the basic ways to reconnect the HMI and PLC. In case after all the steps, the error persists, consult the manufacturer’s technical support or use diagnostic tools such as packet sniffers to track down the problem further.
What should be noted when using HMI and PLC?
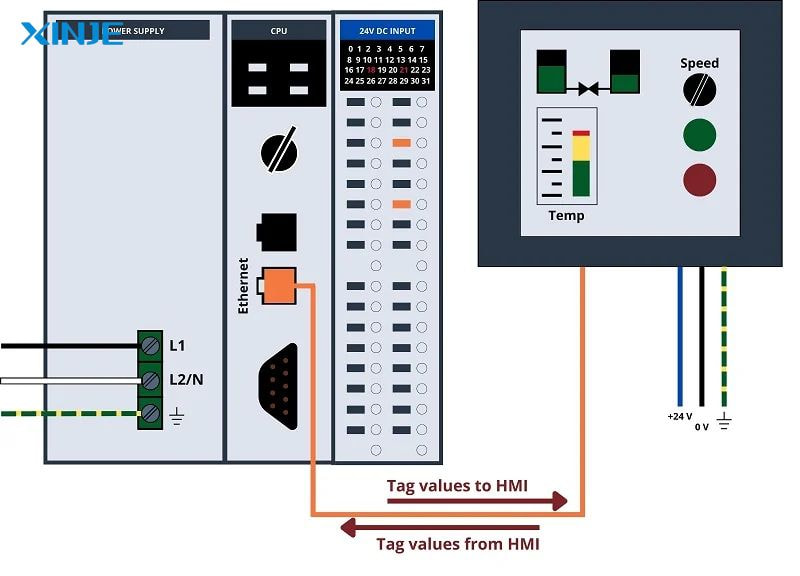

To maintain stable communication between HMI and PLC devices and prevent future disconnections, users should consider the following best practices:
- Design redundancy into the network, such as using dual Ethernet ports or redundant communication paths, and implement failover mechanisms when failures can occur at any time.
- Use industrial-grade components and avoid using commercial network equipment in harsh and large-scale environments.
- Schedule regular maintenance, such as periodic cleaning of ports and connectors, or checking for worn and damaged cables due to the environment.
- Optimize network security and limit unauthorized access to the HMI/PLC system. Additionally, VLAN, password protection, and a firewall can be utilized effectively.
Conclusion
HMI PLC connectivity failures are a common challenge in industrial automation, but with a clear understanding of how these devices communicate and why disconnections occur, you can significantly reduce downtime. Start by diagnosing the physical and network layers, verifying configuration settings, and taking preventative measures to ensure future reliability.
Keeping your HMI and PLC connected is a way to ensure smooth operations, improve productivity, and reduce the risk of costly disruptions. Whether you are an engineer, technician, or plant operator, maintaining this communication link should be a top priority.