What is a communication protocol? A communication protocol is a set of standardized rules that enable electronic devices, such as Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), sensors, and industrial software, to exchange data efficiently and reliably between devices within a manufacturing process.
The prominent function of communication protocols is to ensure that control systems operate cohesively. Whether it is sending signals from an HMI to a conveyor belt or receiving temperature data from a sensor in a cold storage facility, protocols form the digital language that keeps systems synchronized.
What is the function of the Communication Protocol?
The primary function of a communication protocol is to maintain the entire system’s connectivity. In addition, some typical features that need to be mentioned are:
- Data exchange: Ensures accurate and timely data transmission between hardware and software systems.
- Device compatibility: Allows devices from different vendors to operate on the same network.
- Security: Protects transmitted data from unauthorized access or manipulation.
- Efficiency: Reduces latency, information loss, and communication errors in warehouse operations.
Thanks to these outstanding features, the communication protocol has become reliable, ensuring that every command issued by the HMI reaches the robot system on time and that status feedback is sent accurately.
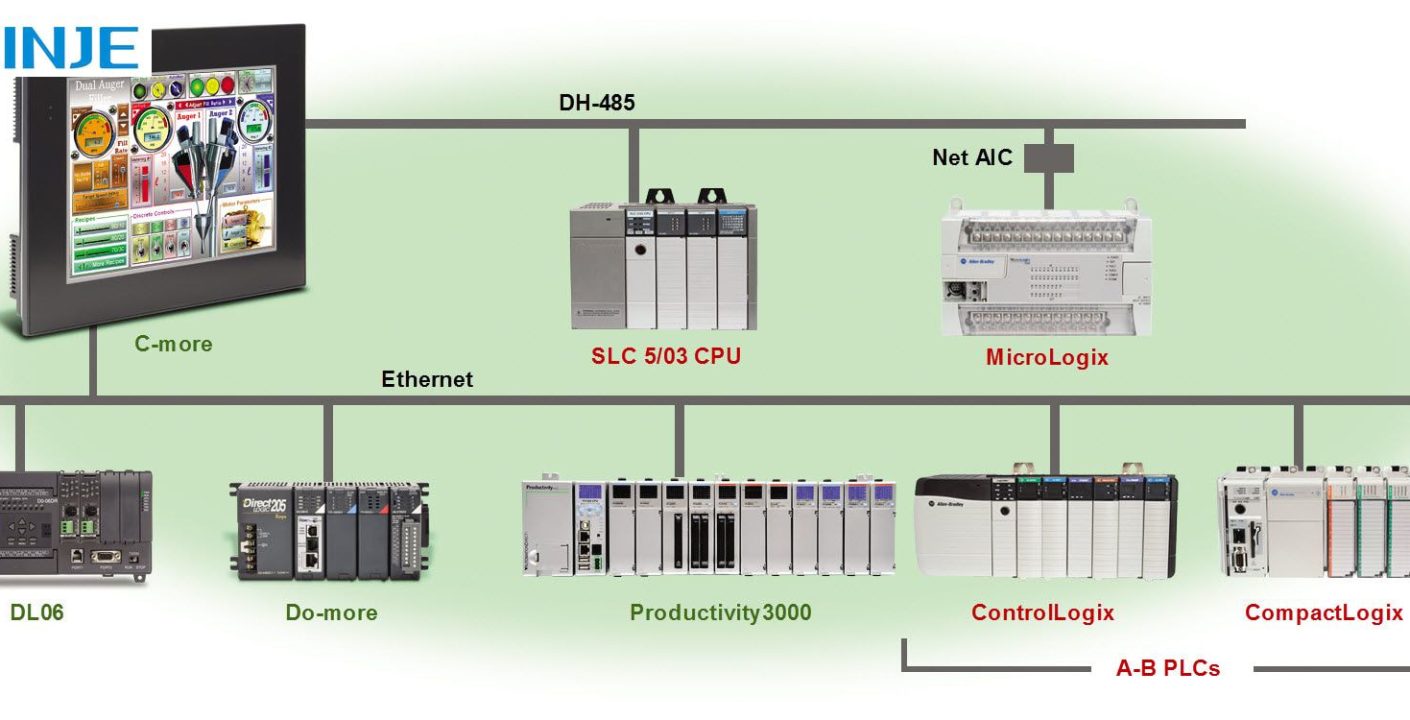
Ethernet
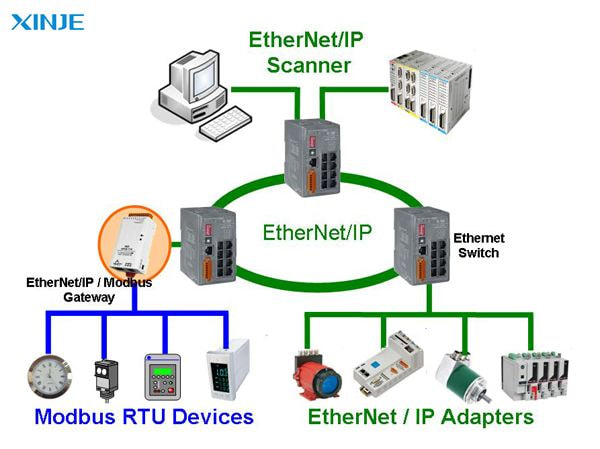

What is Ethernet? Ethernet is one of the most common communication protocols in industrial environments. It uses a wired local area network (LAN) to connect multiple devices and allow real-time data transfer.
Many industrial automation systems, including HMI and PLCs, rely on Industrial Ethernet variants such as Profinet, EtherCAT, and Modbus TCP/IP.
Advantages of Ethernet
- High speed: Ethernet supports fast data transfer rates, which is important for real-time control in automation.
- Scalability: Easy to expand or modify by adding switches and routers.
- Wide applicability: Compatible with most modern industrial hardware.
- Remote access: Allows monitoring and troubleshooting from remote locations.
Disadvantages of Ethernet
- Cabling complexity: Requires structured cabling and planning.
- Signal noise: Can be vulnerable to attacks in environments with strong electromagnetic interference.
- Security risks: If not properly segmented or secured, Ethernet networks can be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
SMTP
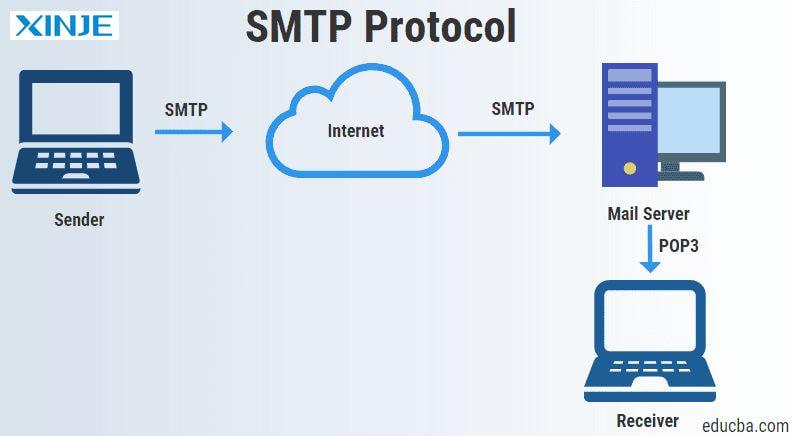

SMTP is commonly used for email transmission but has practical applications in industrial HMI systems. An HMI device can send automated email alerts (such as alarms or errors) to the system administrator or maintenance team for timely detection and correction.
Advantages of SMTP
- Real-time notifications: Help warehouse teams respond quickly to incidents.
- Remote monitoring: Operators receive alerts from anywhere, improving system uptime.
- Easy to configure: Most HMI software supports SMTP setup without the need for third-party tools.
Disadvantages of SMTP
- One-way communication: SMTP is designed for outgoing messages; it does not support real-time, two-way communication.
- Reliant on Internet Access: Requires a stable Internet connection to send notifications.
- Security limitations: Emails can be intercepted if SMTP is not used with SSL/TLS encryption.
Secure Shell or SSH
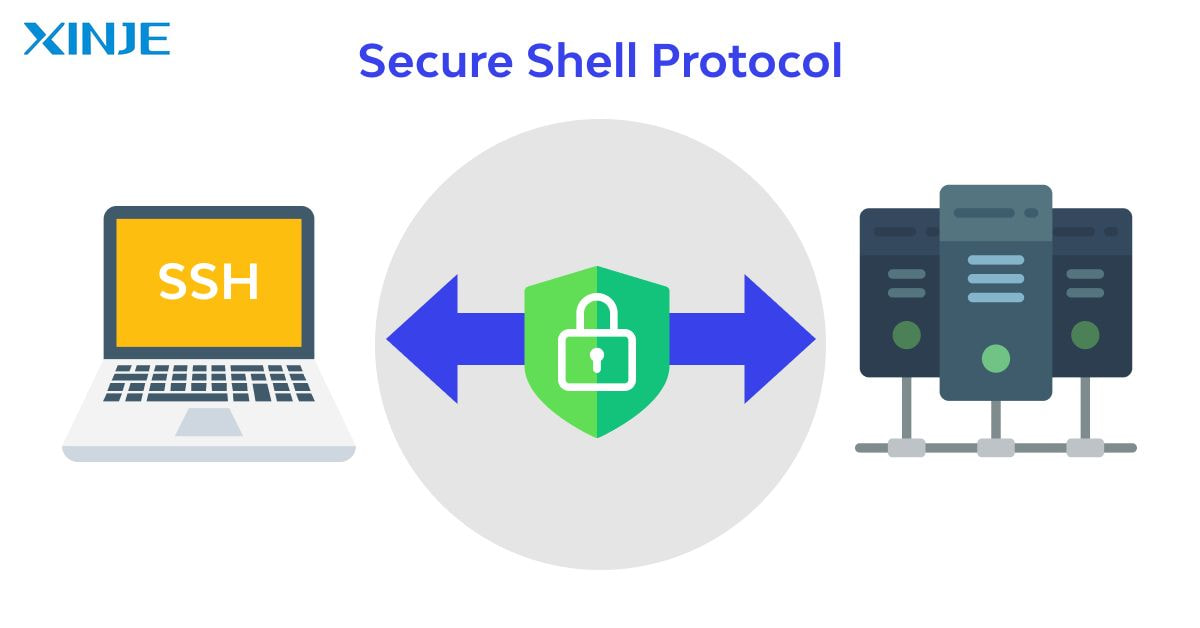

Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol designed to provide secure remote access to devices over an unsecured network. In automation, SSH is commonly used for configuring or troubleshooting Linux-based HMI or edge computing devices.
Advantages of SSH
- End-to-End Encryption: Protects login credentials and data during remote sessions.
- Access Control: Only authenticated users can access devices, increasing security.
- Remote Management: Engineers can manage systems without being physically present on site.
- Script Automation: Allows scheduled scripts for tasks such as backups or diagnostics.
Disadvantages of SSH
- Requires Technical Knowledge: Not all warehouse staff are familiar with SSH commands.
- Risk from Weak Passwords: If poorly configured, SSH can become an attack vector.
- No GUI: SSH is typically command-line only, which may intimidate non-IT staff.
What are Notes when using the Communication Protocol?
When implementing communication protocols in a manufacturing process automation system, operators should consider the following issues to ensure the system operates stably over a long period:
- Compatibility: Operators should verify that their HMIs, PLCs, sensors, and SCADA systems support the selected protocol. Ethernet-based devices must support the same standard.
- Network security: Protect the facility’s communications infrastructure with encrypted protocols (e.g., HTTPS, SSH, SSL) and appropriate user authentication to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Bandwidth management: Ensure the network can handle the volume of communication without delay, especially in systems involving high-speed conveyors or robots, and large-scale operations.
- Clear contingency planning: Designing with redundant and backup communication paths is especially important in large-scale processes where downtime can lead to major losses.
Conclusion
Communication protocols are the backbone of industrial automation systems, enabling seamless integration between HMIs, PLCs, sensors, and control software.
Choosing the right protocol, or combination of protocols, depends on your specific application needs, network environment, and security requirements. As manufacturing becomes smarter and more connected, mastering communication protocols is no longer optional but essential for performance, efficiency, and scalability.